Implementing an ERP system in a fast-growing company is a strategic decision that can transform an organization’s operations. As companies scale, managing complex processes, data, and resources becomes increasingly challenging. An ERP system acts as a central hub, streamlining workflows, providing real-time insights, and enabling data-driven decision-making, ultimately driving growth and efficiency.
This comprehensive guide explores the key considerations involved in implementing an ERP system, from choosing the right system to integrating it with existing technologies, training users, and measuring success. We’ll delve into the challenges faced by fast-growing companies and how an ERP system can address them, empowering businesses to scale effectively and achieve their goals.
The Need for an ERP System
Fast-growing companies often face significant challenges in managing their operations. As businesses expand, they typically experience an increase in data volume, complexity, and the need for greater coordination across departments. These factors can lead to inefficiencies, errors, and a lack of visibility into key business processes. An ERP system can address these challenges by providing a centralized platform for data and processes.
By integrating different departments and functions, an ERP system helps to streamline workflows, improve data accuracy, and enhance communication and collaboration.
Improved Efficiency and Productivity
An ERP system can significantly improve efficiency and productivity in a fast-growing company. By automating repetitive tasks, such as order processing, inventory management, and financial reporting, ERP systems free up employees to focus on more strategic initiatives. This can lead to faster turnaround times, reduced errors, and increased output.
- For example, an ERP system can automate the process of generating purchase orders, tracking inventory levels, and managing supplier relationships. This can help to reduce the time and effort required to procure materials and ensure that the company has the necessary resources on hand.
- An ERP system can also automate the process of generating invoices, tracking payments, and managing accounts receivable. This can help to streamline the accounting process and improve cash flow.
Choosing the Right ERP System
Selecting the right ERP system is a critical decision for fast-growing companies. It’s not just about picking software; it’s about choosing a strategic partner that can support your business’s evolution. The right ERP system can streamline operations, improve efficiency, and provide valuable insights to fuel your growth.
ERP Systems for Fast-Growing Companies
Finding the right ERP system for a fast-growing company involves evaluating several factors. The right ERP system should be scalable, adaptable, and capable of handling increasing data volumes and complex business processes. Here’s a comparison of some popular ERP systems for fast-growing companies:
- NetSuite: A cloud-based ERP system that caters to businesses of all sizes. It offers a comprehensive suite of modules, including financial management, inventory control, CRM, and e-commerce. Its strength lies in its scalability and ability to adapt to growing businesses.
- SAP Business One: A mid-market ERP system known for its robust functionality and deep industry expertise. It’s particularly suitable for manufacturing, distribution, and retail companies. It offers strong integration capabilities and can handle complex business processes.
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central: A cloud-based ERP system designed for small and medium-sized businesses. It’s known for its user-friendly interface and ease of implementation. It offers a wide range of modules, including financial management, sales, and inventory control.
- Odoo: An open-source ERP system that provides a highly customizable platform. It offers a wide range of modules and is suitable for businesses across various industries. It’s known for its flexibility and affordability.
Key Features to Consider
When choosing an ERP system, it’s crucial to consider key features that align with your company’s specific needs. Here are some important factors:
- Scalability: As your company grows, your ERP system should be able to scale with you. It should handle increasing data volumes, user accounts, and complex business processes without compromising performance.
- Integration Capabilities: The ERP system should seamlessly integrate with your existing systems, such as CRM, accounting software, and e-commerce platforms. This ensures data consistency and eliminates manual data entry.
- Industry-Specific Functionalities: Some ERP systems offer industry-specific functionalities tailored to meet the unique needs of specific sectors. This can provide valuable tools and insights for your business.
- User-Friendliness: The system should be easy to use and navigate for all users, regardless of their technical expertise. This ensures adoption and maximizes user productivity.
- Mobile Accessibility: With a growing mobile workforce, the ERP system should be accessible from any device. This allows employees to stay connected and manage tasks on the go.
Factors Influencing Decision-Making
Several factors influence the decision-making process for choosing an ERP system. These factors should be carefully considered to ensure you select a system that meets your present and future needs:
- Company Size: Different ERP systems cater to different company sizes. Small businesses may need a simpler system with basic functionalities, while larger companies may require a more robust system with advanced features.
- Industry: Different industries have specific needs and requirements. For example, a manufacturing company may need a system with strong inventory management capabilities, while a retail company may require a system with robust point-of-sale functionality.
- Budget: ERP systems come at various price points. It’s essential to set a budget and evaluate systems that fit within your financial constraints.
- Long-Term Growth Plans: Your ERP system should support your company’s long-term growth plans. Consider your future needs, such as expanding into new markets or launching new product lines.
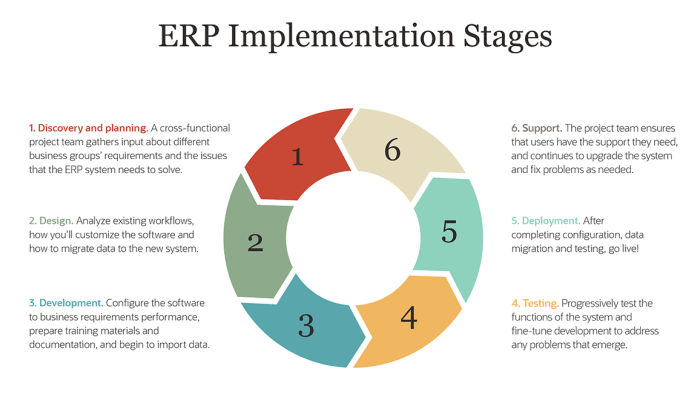
Implementing the ERP System
The implementation of an ERP system is a complex and multifaceted process that requires careful planning, meticulous execution, and ongoing monitoring. A successful ERP implementation can significantly streamline operations, improve efficiency, and provide valuable insights into business performance. However, failing to properly implement an ERP system can result in significant disruptions, financial losses, and a negative impact on employee morale.
This section will provide a step-by-step guide to implementing an ERP system in a fast-growing company.
Implementing the ERP System
Implementing an ERP system is a journey that involves several distinct phases, each with its own set of challenges and opportunities. This process can be broken down into four main phases: Planning, Configuration, Training, and Go-Live.
Planning Phase
The planning phase is crucial for setting the foundation for a successful ERP implementation. This phase involves defining project scope, establishing clear goals, and creating a detailed implementation plan.
| Milestone | Responsibility | Description | Deliverables |
|---|---|---|---|
| Define Project Scope | Project Manager, Key Stakeholders | Identify the specific business processes and departments that will be impacted by the ERP system. | Project Charter, Scope Document |
| Establish Project Goals | Project Manager, Key Stakeholders | Define the desired outcomes of the ERP implementation, such as improved efficiency, reduced costs, or enhanced visibility. | Project Goals Document |
| Develop Implementation Plan | Project Manager, Implementation Team | Create a detailed plan that Artikels the project timeline, resources, and key milestones. | Implementation Plan |
| Identify and Analyze Risks | Project Manager, Implementation Team | Assess potential risks and develop mitigation strategies to minimize their impact. | Risk Assessment Report |
Configuration Phase
The configuration phase involves customizing the ERP system to meet the specific needs of the company. This phase requires close collaboration between the implementation team and the ERP vendor.
| Milestone | Responsibility | Description | Deliverables |
|---|---|---|---|
| Configure System Settings | Implementation Team, ERP Vendor | Customize system settings, such as user roles, security permissions, and data validation rules. | System Configuration Documents |
| Map Business Processes | Implementation Team, Business Users | Map existing business processes to the ERP system’s functionality. | Process Mapping Documents |
| Develop Data Migration Plan | Implementation Team, IT Team | Create a plan for transferring data from existing systems to the new ERP system. | Data Migration Plan |
| Test System Functionality | Implementation Team, Business Users | Conduct thorough testing to ensure that the ERP system meets the company’s requirements. | Test Results Reports |
Training Phase
The training phase is crucial for ensuring that employees are comfortable and proficient in using the new ERP system. Effective training can minimize resistance to change and promote user adoption.
| Milestone | Responsibility | Description | Deliverables |
|---|---|---|---|
| Develop Training Materials | Implementation Team, ERP Vendor | Create comprehensive training materials, including manuals, tutorials, and online courses. | Training Materials |
| Conduct Training Sessions | Implementation Team, Trainers | Deliver interactive training sessions to employees, covering system functionality and best practices. | Training Attendance Records |
| Provide Ongoing Support | Implementation Team, Help Desk | Offer ongoing support to employees through FAQs, user guides, and dedicated help desk services. | Support Documentation |
| Evaluate Training Effectiveness | Implementation Team | Assess the effectiveness of training programs and identify areas for improvement. | Training Evaluation Reports |
Go-Live Phase
The go-live phase marks the transition from the old system to the new ERP system. This phase requires careful planning and coordination to ensure a smooth transition.
| Milestone | Responsibility | Description | Deliverables |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prepare for Go-Live | Implementation Team, IT Team | Complete final testing, finalize data migration, and ensure all systems are ready for launch. | Go-Live Readiness Checklist |
| Go-Live Event | Implementation Team, IT Team | Launch the new ERP system, providing support and guidance to users. | Go-Live Event Log |
| Monitor System Performance | Implementation Team, IT Team | Continuously monitor the ERP system’s performance, identify any issues, and implement corrective actions. | System Performance Reports |
| Provide Post-Go-Live Support | Implementation Team, Help Desk | Offer ongoing support to users, addressing any questions or concerns they may have. | Support Ticket Records |
Stakeholder Engagement, Communication, and Change Management
Stakeholder engagement, communication, and change management are essential for a successful ERP implementation. Failure to effectively engage stakeholders, communicate changes, and manage resistance can lead to project delays, budget overruns, and user dissatisfaction.
Stakeholder Engagement
It is crucial to involve all key stakeholders in the ERP implementation process, including:
- Executive Management: Provide direction and support, allocate resources, and approve key decisions.
- Business Users: Provide input on system requirements, participate in testing, and provide feedback on system usability.
- IT Department: Ensure system integration, data migration, and technical support.
- ERP Vendor: Provide technical expertise, training, and ongoing support.
Communication
Effective communication is essential for keeping stakeholders informed about the progress of the ERP implementation. Regular communication can build trust, address concerns, and ensure everyone is aligned on project goals.
- Project Meetings: Hold regular meetings to discuss project status, address issues, and solicit feedback.
- Email Updates: Send periodic email updates to keep stakeholders informed about key milestones and achievements.
- Training Materials: Provide comprehensive training materials that clearly explain system functionality and best practices.
- Help Desk Support: Offer dedicated help desk support to address user questions and concerns.
Change Management
Change management is crucial for minimizing resistance to the new ERP system. This involves understanding the impact of change on employees, addressing concerns, and providing support to help them adapt.
- Communicate the Benefits: Clearly articulate the benefits of the new ERP system, such as improved efficiency, reduced costs, or enhanced visibility.
- Provide Training: Offer comprehensive training to help employees learn how to use the new system effectively.
- Address Concerns: Actively listen to employee concerns and address them in a timely and professional manner.
- Provide Support: Offer ongoing support to employees during the transition period.
Integrating with Existing Systems
Integrating an ERP system with your existing systems, such as CRM, accounting software, and inventory management systems, is a crucial step in maximizing the benefits of your ERP implementation. It enables seamless data flow, reduces redundancy, and improves overall efficiency. However, this integration process can present unique challenges.
Challenges of Integration
Integrating an ERP system with existing systems can pose significant challenges. The primary hurdle is ensuring data consistency and accuracy across different platforms. Each system may have its own data structure, formats, and definitions, leading to potential discrepancies. Additionally, data synchronization between systems can be complex, requiring careful mapping and real-time updates. Moreover, integrating legacy systems with a new ERP can be particularly challenging due to their outdated technology and potential lack of API support.
Strategy for Seamless Integration
A well-defined integration strategy is essential for successful ERP implementation. The first step is to identify all existing systems that need to be integrated with the ERP. Conduct a thorough analysis of each system’s data structure, formats, and functionalities. This analysis will help you map data fields and define integration points.
- Data Mapping: Create a detailed mapping document that clearly defines how data will be transferred between systems. This includes identifying corresponding fields, data types, and conversion rules.
- Integration Method: Choose the appropriate integration method based on the complexity and requirements of the integration. Common methods include real-time integration, batch processing, and message queues.
- Data Quality Management: Implement data quality checks and validation rules to ensure data accuracy and consistency across all integrated systems.
- Testing and Validation: Thoroughly test the integration process to identify and resolve any issues before going live.
Best Practices for Integration
To minimize disruptions and maximize the benefits of integration, follow these best practices:
- Start Small: Begin with integrating a few key systems and gradually expand the integration scope. This allows for a phased approach, minimizing risks and enabling early success.
- Involve Stakeholders: Engage all relevant stakeholders, including IT teams, business users, and system vendors, in the integration process. Their input is crucial for identifying potential challenges and ensuring a successful implementation.
- Use Integration Tools: Leverage specialized integration tools and middleware to facilitate seamless data exchange between systems. These tools can simplify the integration process and improve data quality.
- Documentation: Maintain comprehensive documentation of the integration process, including data mapping, integration methods, and testing results. This documentation will be invaluable for troubleshooting and future maintenance.
Training and Support
The success of an ERP system implementation goes beyond just choosing the right software and setting it up. Training and ongoing support are crucial elements that ensure users can effectively utilize the system, maximizing its benefits and driving long-term success.
Training Programs
Comprehensive training programs are essential for all users, from managers and employees to IT staff. Proper training helps users understand the system’s functionality, navigate its features, and ultimately contribute to the organization’s goals.
Different Training Methods
The most effective training methods depend on the user group’s needs and learning styles. Here’s a breakdown of popular training methods and their suitability:
| Training Method | Suitable for |
|---|---|
| Classroom Training | Large groups, new hires, and those needing structured learning |
| Online Courses | Self-paced learning, individual preferences, and flexible schedules |
| On-the-Job Training | Experienced users, practical application, and quick skill development |
| Mentorship Programs | One-on-one support, personalized guidance, and ongoing knowledge transfer |
| Job Aids and Documentation | Quick reference guides, FAQs, and support for common tasks |
Ongoing Support and Maintenance, Implementing an ERP system in a fast-growing company
An ERP system is a dynamic tool that requires ongoing support and maintenance to ensure it remains functional, secure, and optimized for the evolving needs of the organization.
Importance of Ongoing Support
Regular maintenance, including software updates, security patches, and performance tuning, is crucial for maintaining the system’s stability and preventing potential issues. Additionally, dedicated support teams can provide timely assistance to users facing challenges or needing help with specific tasks.
Types of Support
Support can be provided through various channels, including:* Helpdesk: A centralized point of contact for users to report issues and seek assistance.
Knowledge Base
An online repository of FAQs, user guides, and troubleshooting tips.
Community Forums
Online platforms where users can connect, share knowledge, and find solutions to common problems.
Dedicated Support Team
A team of professionals trained to provide specialized support for specific ERP modules or functionalities.
Measuring Success
Measuring the success of your ERP implementation is crucial to ensure that the system delivers the expected benefits and return on investment (ROI). By tracking key performance indicators (KPIs), you can monitor progress, identify areas for improvement, and demonstrate the value of the ERP system to stakeholders.
Identifying Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
To measure the success of your ERP implementation, you need to identify relevant KPIs that align with your business goals and objectives. These KPIs should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
- Financial KPIs: These KPIs measure the financial impact of the ERP implementation. Examples include:
- Return on Investment (ROI): Measures the financial return generated by the ERP system compared to the initial investment.
- Cost Savings: Tracks reductions in operational costs, such as labor, inventory, and administrative expenses.
- Increased Revenue: Measures the growth in revenue generated by the ERP system, such as through improved efficiency and customer satisfaction.
- Operational KPIs: These KPIs measure the efficiency and effectiveness of the ERP system in supporting business processes. Examples include:
- Order Fulfillment Rate: Tracks the percentage of orders that are fulfilled on time and accurately.
- Inventory Turnover Rate: Measures the number of times inventory is sold and replaced within a specific period.
- Cycle Time: Tracks the time it takes to complete specific business processes, such as order processing or production.
- Customer KPIs: These KPIs measure the impact of the ERP system on customer satisfaction and loyalty. Examples include:
- Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT): Measures customer satisfaction with the products or services delivered by the business.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): Measures customer loyalty and willingness to recommend the business to others.
- Customer Retention Rate: Tracks the percentage of customers who continue to do business with the company over time.
Relationship Between KPIs, Desired Outcomes, and Measurement Methods
| KPI | Desired Outcome | Measurement Method |
|---|---|---|
| Return on Investment (ROI) | Increased profitability and financial performance | Calculate the ratio of net profit to total investment. |
| Order Fulfillment Rate | Improved order accuracy and on-time delivery | Track the percentage of orders shipped on time and without errors. |
| Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT) | Enhanced customer satisfaction and loyalty | Conduct surveys or collect feedback from customers on their experience. |
Analyzing Data and Making Adjustments
Once you have collected data on your KPIs, you need to analyze it to identify trends and patterns. This analysis will help you understand the impact of the ERP system on your business and identify areas for improvement. You can use various data analysis techniques, such as:
- Trend Analysis: Tracks changes in KPIs over time to identify patterns and trends.
- Comparative Analysis: Compares KPIs before and after the ERP implementation to assess the impact of the system.
- Root Cause Analysis: Investigates the underlying causes of deviations in KPIs to identify areas for improvement.
Based on your data analysis, you can make adjustments to the ERP system to optimize its performance and maximize its impact on your business. For example, you might:
- Improve system configuration: Adjust system settings to streamline processes and improve efficiency.
- Enhance user training: Provide additional training to users to improve their understanding and utilization of the system.
- Optimize business processes: Re-engineer business processes to take advantage of the capabilities of the ERP system.
By carefully planning, implementing, and managing an ERP system, fast-growing companies can unlock significant advantages. The journey may present challenges, but the rewards are substantial. From improved efficiency and productivity to enhanced data visibility and informed decision-making, a well-integrated ERP system empowers businesses to thrive in a dynamic environment. By embracing the power of an ERP system, fast-growing companies can position themselves for sustained success and continued growth.
Questions Often Asked: Implementing An ERP System In A Fast-growing Company
What are the potential risks of implementing an ERP system?
Potential risks include high implementation costs, disruption to existing workflows, resistance to change from employees, and data migration issues. However, careful planning, communication, and training can mitigate these risks.
How long does it typically take to implement an ERP system?
Implementation timelines vary depending on the complexity of the system, company size, and integration requirements. Generally, it can take anywhere from a few months to a year or more.
What is the return on investment (ROI) of an ERP system?
The ROI of an ERP system can be significant, resulting in increased efficiency, reduced costs, improved customer satisfaction, and better decision-making. However, it’s crucial to carefully track and measure the benefits to quantify the ROI.
What are the key considerations when choosing an ERP vendor?
Key considerations include the vendor’s experience, industry expertise, scalability of the system, integration capabilities, pricing, and support services. It’s essential to choose a vendor that aligns with the company’s specific needs and long-term growth plans.