ERP systems for retail businesses are transforming the industry by providing a centralized platform for managing critical operations. These systems offer a comprehensive suite of tools to address common retail challenges, from inventory management and point-of-sale (POS) to customer relationship management (CRM) and supply chain optimization.
By integrating various modules, ERP systems enable retailers to gain real-time insights into their business, streamline processes, and enhance customer experiences. From optimizing inventory levels to improving order fulfillment and providing personalized recommendations, ERP systems empower businesses to make data-driven decisions and achieve significant improvements in efficiency and profitability.
Introduction to ERP Systems for Retail Businesses
Running a retail business can be complex and challenging, especially in today’s competitive market. Managing inventory, tracking sales, and keeping up with customer demands requires efficient and integrated systems. This is where Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems come into play. ERP systems are software applications that help businesses manage and integrate various aspects of their operations, including finance, human resources, supply chain, and customer relationship management (CRM).
They provide a centralized platform for data storage, analysis, and decision-making, streamlining processes and improving overall efficiency.
Benefits of Implementing an ERP System for Retail Businesses
Implementing an ERP system offers numerous benefits for retail businesses, leading to improved efficiency, enhanced inventory management, and better customer service.
- Improved Efficiency: ERP systems automate repetitive tasks, such as order processing, inventory management, and financial reporting, freeing up employees to focus on more strategic initiatives. This can lead to increased productivity and reduced operational costs.
- Enhanced Inventory Management: ERP systems provide real-time visibility into inventory levels, helping retailers optimize stock levels and avoid stockouts or overstocking. They also enable better forecasting and planning, ensuring that the right products are available at the right time.
- Better Customer Service: By integrating customer data and sales information, ERP systems allow retailers to provide personalized customer experiences. They can track customer preferences, purchase history, and interactions, enabling them to offer targeted promotions and recommendations.
- Improved Financial Management: ERP systems provide comprehensive financial reporting and analysis capabilities, allowing retailers to track revenue, expenses, and profitability. They also facilitate better budgeting and financial planning.
Key Features of ERP Systems for Retail
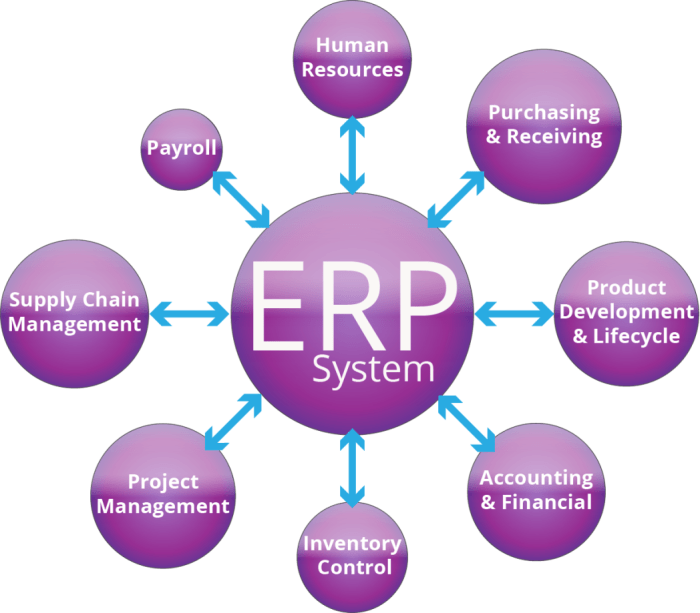
An ERP system designed for retail businesses incorporates modules that cater to the unique needs of the industry. These modules work together seamlessly, providing a comprehensive view of the entire retail operation.
Inventory Management
Inventory management is a critical aspect of any retail business. ERP systems for retail provide robust inventory management modules that help businesses track inventory levels, manage stock movements, and optimize inventory levels.
- Real-time Inventory Tracking: ERP systems provide real-time visibility into inventory levels across all locations, ensuring accurate stock counts and preventing stockouts.
- Automated Purchase Orders: Automated purchase order generation based on pre-defined reorder points ensures timely replenishment and minimizes stock shortages.
- Inventory Optimization: Advanced inventory optimization algorithms help retailers determine the optimal stock levels for each product, minimizing holding costs and maximizing sales.
For example, an ERP system can automatically generate a purchase order for a specific product when its inventory level falls below a predetermined threshold, ensuring that the retailer always has enough stock on hand to meet customer demand.
Point-of-Sale (POS)
The POS module is the heart of any retail operation. It handles transactions, manages customer data, and provides valuable insights into sales performance.
- Transaction Processing: The POS module facilitates quick and accurate transaction processing, including cash, credit card, and other payment methods.
- Customer Data Capture: The POS system captures customer data, such as purchase history and contact information, which can be used for targeted marketing and customer loyalty programs.
- Sales Reporting: The POS module provides detailed sales reports, including revenue, product performance, and customer demographics, enabling retailers to analyze sales trends and make informed decisions.
A retailer can use the POS module to track customer preferences and offer personalized recommendations based on their past purchases, leading to increased customer satisfaction and sales.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
CRM modules help retailers manage customer interactions and build lasting relationships.
- Customer Database Management: CRM systems provide a centralized database for storing customer information, including contact details, purchase history, and preferences.
- Marketing Automation: CRM systems enable retailers to automate marketing campaigns, such as email newsletters, targeted promotions, and loyalty programs, to engage customers and drive sales.
- Customer Service Management: CRM modules provide tools for managing customer inquiries, complaints, and feedback, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
For example, a retailer can use the CRM module to segment customers based on their purchase history and send targeted promotions to specific groups, increasing the effectiveness of their marketing efforts.
Supply Chain Management
The supply chain management module helps retailers manage their entire supply chain, from procurement to delivery.
- Supplier Management: The module provides tools for managing supplier relationships, including negotiation, order placement, and payment processing.
- Logistics Optimization: The module optimizes logistics operations, including transportation, warehousing, and distribution, ensuring timely and cost-effective delivery of goods.
- Demand Forecasting: The module helps retailers forecast demand based on historical data and market trends, enabling them to optimize inventory levels and avoid stockouts.
Retailers can use the supply chain management module to track shipments in real-time, identify potential delays, and take proactive measures to ensure on-time delivery, reducing costs and improving customer satisfaction.
Implementation and Integration of ERP Systems
Implementing an ERP system in a retail business is a complex and multifaceted process that requires careful planning, execution, and ongoing management. It involves a series of steps that must be undertaken in a coordinated and strategic manner to ensure successful adoption and utilization of the system. This section will delve into the key steps involved in implementing an ERP system in a retail business, including planning, customization, data migration, and training.
Additionally, it will explore the challenges and considerations for integrating an ERP system with existing retail systems and technologies.
Implementation Steps
Implementing an ERP system involves a series of well-defined steps that must be followed to ensure a successful rollout. The implementation process typically includes the following stages:
- Planning: This stage involves defining the project scope, objectives, and goals. It is essential to clearly understand the business requirements, the functionalities needed from the ERP system, and the desired outcomes. A comprehensive project plan should be developed, outlining the timeline, budget, resources, and key stakeholders involved.
- Customization: Once the ERP system is selected, it needs to be customized to meet the specific needs of the retail business. This involves configuring the system settings, customizing modules, and tailoring workflows to align with the company’s processes and practices. Customization ensures that the ERP system effectively supports the retail business operations.
- Data Migration: This stage involves transferring data from existing systems to the new ERP system. This includes customer data, product information, sales records, inventory data, and financial records. Data migration requires careful planning and execution to ensure data integrity, accuracy, and completeness.
- Training: Once the ERP system is implemented, it is crucial to provide comprehensive training to all users. Training should cover system functionalities, navigation, data entry, reporting, and best practices for using the ERP system effectively.
- Testing and Go-Live: Before the ERP system is launched, it needs to be thoroughly tested to ensure it meets the business requirements and functions as expected. This includes testing data migration, system performance, and user workflows. Once the system is deemed ready, it can be launched or go live.
- Post-Implementation Support: After the ERP system is implemented, ongoing support is essential to address user queries, resolve issues, and ensure system stability. This may include providing technical support, user training, and system updates.
Integration Challenges
Integrating an ERP system with existing retail systems and technologies can present several challenges:
- Data Compatibility: Different systems may use different data formats and structures, making it challenging to integrate data seamlessly. This requires careful data mapping and transformation to ensure data consistency and accuracy.
- System Interoperability: Ensuring that different systems can communicate and exchange data effectively is crucial for successful integration. This may involve using middleware or APIs to facilitate data transfer and synchronization.
- Security Concerns: Integrating different systems raises security concerns, as data needs to be protected from unauthorized access and breaches. Secure data transfer protocols and access controls are essential to mitigate these risks.
- Complexity and Cost: Integrating an ERP system with multiple existing systems can be a complex and costly undertaking, requiring significant time, effort, and resources.
Step-by-Step Implementation Guide
Implementing an ERP system is a complex process that requires careful planning and execution. Here is a step-by-step guide for implementing an ERP system in a retail business:
- Define Project Scope and Objectives: Clearly define the scope of the ERP implementation project, including the business units, processes, and systems to be covered. Establish clear project objectives and desired outcomes.
- Select an ERP System: Research and evaluate different ERP systems based on your business needs, budget, and industry requirements. Consider factors such as functionality, scalability, user-friendliness, and vendor support.
- Develop a Project Plan: Create a comprehensive project plan that Artikels the timeline, budget, resources, and key milestones. Define roles and responsibilities for team members.
- Customize the ERP System: Configure the ERP system settings, customize modules, and tailor workflows to align with your business processes and practices. Ensure that the system meets your specific requirements.
- Migrate Data: Plan and execute data migration from existing systems to the new ERP system. Ensure data integrity, accuracy, and completeness.
- Train Users: Provide comprehensive training to all users on system functionalities, navigation, data entry, reporting, and best practices.
- Test the System: Thoroughly test the ERP system to ensure it meets business requirements and functions as expected. Test data migration, system performance, and user workflows.
- Go Live: Launch the ERP system and provide ongoing support to users. Address user queries, resolve issues, and ensure system stability.
Key Milestones and Best Practices
Implementing an ERP system is a major undertaking, and it is essential to establish key milestones and follow best practices to ensure successful implementation.
- Establish Clear Communication: Maintain open and transparent communication with all stakeholders throughout the implementation process. Regularly share updates, address concerns, and solicit feedback.
- Involve Key Stakeholders: Engage key stakeholders from different departments and levels of the organization in the implementation process. This ensures that the ERP system meets the needs of all users and aligns with business goals.
- Manage Change Effectively: Implement change management strategies to minimize resistance and facilitate user adoption. Provide clear communication, training, and support to help users adapt to the new system.
- Focus on User Adoption: Ensure that the ERP system is user-friendly and intuitive to encourage user adoption. Provide ongoing training, support, and resources to help users become proficient in using the system.
- Continuously Improve: Regularly review and assess the ERP system performance and identify areas for improvement. Make necessary adjustments and updates to optimize system functionality and meet evolving business needs.
Benefits and Impact of ERP Systems on Retail Operations

ERP systems are designed to provide a comprehensive view of retail operations, offering real-time insights into inventory levels, customer behavior, and sales performance. This visibility allows businesses to make informed decisions, optimize processes, and improve overall efficiency.
Streamlining Retail Operations
ERP systems act as a central hub for all retail operations, integrating data from various departments, such as sales, inventory, finance, and customer service. This integration eliminates silos and ensures consistent data flow, enabling real-time monitoring of key performance indicators (KPIs).
- Inventory Management: ERP systems provide real-time visibility into inventory levels, allowing retailers to track stock movements, identify slow-moving items, and predict future demand. This information helps optimize inventory planning, reduce stockouts, and minimize holding costs.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): ERP systems integrate with CRM modules to provide a comprehensive view of customer interactions, purchase history, and preferences. This data helps personalize customer experiences, tailor marketing campaigns, and enhance customer loyalty.
- Sales Performance Tracking: ERP systems track sales data, providing insights into sales trends, product performance, and customer behavior. This information allows retailers to identify best-selling products, optimize pricing strategies, and forecast future sales.
Improving Inventory Accuracy and Reducing Stockouts
Accurate inventory data is crucial for efficient retail operations. ERP systems help improve inventory accuracy by:
- Real-Time Inventory Tracking: ERP systems provide real-time updates on inventory levels, eliminating the need for manual counting and reducing discrepancies.
- Automated Purchase Orders: ERP systems automate purchase orders based on predefined thresholds, ensuring timely replenishment and minimizing stockouts.
- Advanced Forecasting: ERP systems use historical data and predictive analytics to forecast demand, enabling retailers to optimize inventory levels and reduce overstocking.
Optimizing Supply Chain Efficiency
ERP systems streamline the supply chain by:
- Vendor Management: ERP systems centralize vendor information, track purchase orders, and manage payments, improving communication and collaboration with suppliers.
- Transportation Management: ERP systems optimize transportation routes, track shipments, and manage logistics, reducing delivery times and costs.
- Demand Planning: ERP systems use historical data and predictive analytics to forecast demand, enabling retailers to optimize production and procurement processes.
Enhancing Customer Experience, ERP systems for retail businesses
ERP systems contribute to a better customer experience by:
- Personalized Recommendations: By analyzing customer purchase history and preferences, ERP systems can provide personalized product recommendations, increasing sales and customer satisfaction.
- Improved Order Fulfillment: ERP systems streamline order processing, ensuring accurate and timely delivery, reducing customer wait times and improving satisfaction.
- Enhanced Customer Service: ERP systems provide customer service representatives with access to customer information, order history, and product details, enabling them to provide faster and more efficient support.
Future Trends in ERP Systems for Retail
The retail landscape is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer preferences. ERP systems are at the forefront of this evolution, adapting to meet the growing demands of modern retailers. Emerging trends in ERP systems are shaping the future of retail operations and customer experiences, offering exciting opportunities for businesses to optimize efficiency, enhance customer engagement, and gain a competitive edge.
Cloud-Based ERP Solutions
Cloud-based ERP solutions are becoming increasingly popular among retailers due to their scalability, affordability, and accessibility. Cloud-based ERP systems are hosted on remote servers and accessed through the internet, eliminating the need for expensive hardware and software installations. This flexibility allows retailers to scale their ERP system up or down as needed, making it a cost-effective option for businesses of all sizes.
- Reduced IT Costs: Cloud-based ERP systems eliminate the need for on-premises infrastructure, reducing IT costs associated with hardware, software, and maintenance.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud-based ERP systems can be easily scaled up or down to meet changing business needs, making them ideal for growing businesses or those experiencing seasonal fluctuations.
- Accessibility: Cloud-based ERP systems can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, enabling employees to work remotely and collaborate effectively.
- Automatic Updates: Cloud-based ERP systems are automatically updated with the latest features and security patches, ensuring that retailers always have access to the most up-to-date technology.
Mobile Accessibility
Mobile accessibility is another key trend in ERP systems for retail. Retailers are increasingly using mobile devices to access their ERP systems, allowing them to manage operations and access data on the go. Mobile ERP apps provide real-time insights into inventory levels, customer orders, and sales performance, enabling managers to make informed decisions quickly and efficiently.
- Improved Decision-Making: Mobile ERP apps provide real-time data and insights, enabling managers to make informed decisions quickly and efficiently.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Mobile accessibility facilitates seamless communication and collaboration between employees, regardless of their location.
- Increased Productivity: Mobile ERP apps streamline tasks and processes, allowing employees to work more efficiently and productively.
- Improved Customer Service: Mobile ERP apps enable customer service representatives to access customer information and order history quickly, improving customer satisfaction.
Artificial Intelligence Integration
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming the retail industry, and ERP systems are incorporating AI capabilities to enhance operational efficiency and customer engagement. AI-powered ERP systems can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and trends, enabling retailers to optimize inventory management, personalize customer experiences, and improve supply chain efficiency.
- Predictive Analytics: AI algorithms can analyze historical data and current trends to predict future demand, enabling retailers to optimize inventory levels and reduce stockouts.
- Personalized Customer Experiences: AI-powered ERP systems can analyze customer data to personalize product recommendations, marketing campaigns, and customer service interactions.
- Automated Processes: AI can automate repetitive tasks, such as order fulfillment, inventory management, and data entry, freeing up employees to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Fraud Detection: AI algorithms can detect fraudulent transactions and identify potential security risks, protecting retailers from financial losses.
In conclusion, ERP systems are essential for retail businesses seeking to thrive in today’s competitive landscape. By embracing these powerful tools, retailers can unlock new levels of efficiency, improve customer satisfaction, and gain a competitive edge. As technology continues to evolve, the future of ERP systems in retail holds immense promise for further innovation and growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key benefits of using an ERP system for a retail business?
ERP systems offer numerous benefits, including improved efficiency, enhanced inventory management, streamlined operations, better customer service, and data-driven decision-making.
How much does it cost to implement an ERP system?
The cost of implementing an ERP system varies depending on factors such as the size of the business, the chosen solution, and the level of customization required. It’s essential to carefully evaluate different options and consider the long-term return on investment.
What are some popular ERP systems for retail businesses?
Some popular ERP systems for retail businesses include SAP, Oracle, Microsoft Dynamics 365, NetSuite, and Acumatica. Each system has its own strengths and weaknesses, so it’s important to choose the one that best aligns with your specific needs and budget.