ERP integration with other business applications sets the stage for streamlined operations, improved efficiency, and enhanced data visibility across your entire organization. This strategic approach connects disparate systems, creating a unified platform that eliminates data silos, automates processes, and fosters real-time collaboration.
Imagine a scenario where customer orders flow seamlessly from your e-commerce platform to your ERP system, triggering automated inventory updates and production schedules. This is just one example of how ERP integration can transform your business, enabling you to respond to market demands with agility and precision.
The Importance of ERP Integration
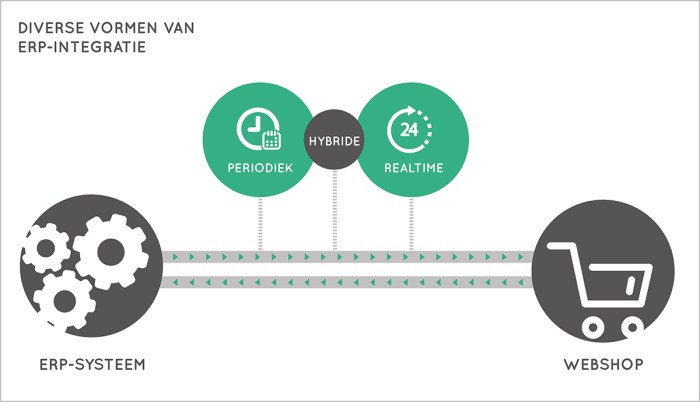
In today’s dynamic business environment, seamless integration of enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems with other business applications is no longer a luxury but a necessity. ERP integration empowers organizations to optimize operations, enhance efficiency, and gain a competitive edge.
Integrating ERP systems with other business applications creates a unified platform that breaks down data silos and fosters collaboration across departments. This interconnectedness allows for real-time data sharing, automated processes, and improved decision-making. Furthermore, integration eliminates the need for manual data entry, reduces errors, and streamlines workflows, resulting in significant cost savings and productivity gains.
Benefits of ERP Integration
The integration of ERP systems with other business applications offers a wide range of benefits that can significantly impact an organization’s performance. These benefits include:
- Improved Data Accuracy and Consistency: Integration eliminates data duplication and inconsistencies by providing a single source of truth, ensuring accurate and reliable information across the organization.
- Enhanced Visibility and Transparency: Integrated systems offer real-time visibility into operations, allowing stakeholders to track key metrics, monitor performance, and identify potential issues proactively.
- Streamlined Workflows and Automation: Automating repetitive tasks and processes through integration frees up employees to focus on more strategic activities, boosting productivity and efficiency.
- Improved Collaboration and Communication: Integration facilitates seamless communication and collaboration among departments, breaking down silos and fostering a more unified organizational culture.
- Reduced Costs and Increased Efficiency: Integration streamlines operations, eliminates manual processes, and minimizes errors, leading to significant cost savings and improved efficiency.
- Better Customer Service: By integrating with customer relationship management (CRM) systems, ERP systems can provide a comprehensive view of customer interactions, enabling organizations to deliver personalized and efficient service.
- Improved Decision-Making: Access to real-time, accurate data from integrated systems empowers organizations to make informed and data-driven decisions, leading to better strategic planning and execution.
Real-World Examples of ERP Integration
Numerous organizations across various industries have successfully implemented ERP integration and reaped significant benefits. Here are some real-world examples:
- Manufacturing: A manufacturing company integrated its ERP system with its production planning and scheduling software, enabling real-time visibility into production lines, inventory levels, and supply chain performance. This integration resulted in optimized production schedules, reduced downtime, and improved efficiency.
- Retail: A retail chain integrated its ERP system with its point-of-sale (POS) system, allowing for centralized inventory management, real-time sales tracking, and improved customer insights. This integration led to increased sales, reduced stockouts, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
- Healthcare: A healthcare provider integrated its ERP system with its electronic health record (EHR) system, streamlining patient data management, billing processes, and appointment scheduling. This integration improved patient care, reduced administrative burden, and enhanced financial performance.
Types of Business Applications to Integrate with ERP
ERP systems are designed to be the central hub of an organization’s operations, but they can’t do everything on their own. To maximize their potential, ERP systems are often integrated with other business applications that cater to specific needs. These integrations create a seamless flow of data and processes across different departments and systems, enhancing efficiency and decision-making.Integrating ERP with other applications can streamline operations, reduce manual effort, and improve data accuracy.
This section delves into the different types of business applications commonly integrated with ERP systems, highlighting their key features and integration benefits.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Integrating CRM with ERP can provide a holistic view of customer interactions, from initial contact to post-sales support. This integration allows businesses to:
- Track customer interactions across various channels, including email, phone, and social media, providing a unified customer profile.
- Improve customer service by accessing relevant customer information, order history, and past interactions within the ERP system.
- Personalize marketing campaigns by leveraging customer data from both systems to create targeted and relevant messages.
- Optimize sales processes by streamlining order fulfillment and providing real-time visibility into inventory levels and order status.
Supply Chain Management (SCM)
Integrating SCM with ERP enables businesses to optimize their supply chain operations, from procurement to delivery. This integration allows businesses to:
- Manage inventory levels by tracking real-time inventory data and forecasting future demand based on historical sales patterns.
- Optimize procurement processes by automating purchase orders and managing supplier relationships effectively.
- Streamline logistics and transportation by tracking shipments in real-time and optimizing delivery routes.
- Improve supply chain visibility by providing a comprehensive overview of the entire supply chain, from raw materials to finished goods.
Human Resources Management (HRM), ERP integration with other business applications
Integrating HRM with ERP enables businesses to manage their workforce effectively, from recruitment to payroll. This integration allows businesses to:
- Automate payroll processes by integrating employee data from the ERP system with payroll software, reducing manual errors and improving efficiency.
- Manage employee benefits by providing a centralized platform for managing benefits enrollment, tracking eligibility, and processing claims.
- Streamline recruitment and onboarding by integrating job postings, applications, and employee onboarding processes.
- Improve employee performance management by tracking performance metrics, providing feedback, and facilitating training and development programs.
Financial Management
Integrating financial management applications with ERP provides a comprehensive view of financial data, enabling businesses to:
- Consolidate financial data from different sources into a single platform, providing a unified view of financial performance.
- Automate financial reporting by generating financial statements, budgets, and other reports based on real-time data.
- Improve financial forecasting by leveraging historical data and market trends to predict future financial performance.
- Enhance compliance by automating financial processes and ensuring adherence to regulatory requirements.
E-commerce Platforms
Integrating e-commerce platforms with ERP enables businesses to manage online sales and inventory effectively. This integration allows businesses to:
- Sync product data between the e-commerce platform and the ERP system, ensuring accurate product descriptions and pricing.
- Automate order processing by automatically updating inventory levels and generating invoices upon order placement.
- Manage customer accounts by synchronizing customer information between the e-commerce platform and the ERP system.
- Provide real-time order tracking by integrating order status updates from the ERP system into the e-commerce platform.
Business Intelligence (BI)
Integrating BI with ERP enables businesses to analyze data from various sources, gaining insights into their operations and making data-driven decisions. This integration allows businesses to:
- Create interactive dashboards that provide real-time insights into key performance indicators (KPIs).
- Analyze historical data to identify trends and patterns, helping businesses make informed decisions.
- Generate customized reports based on specific business requirements, providing valuable insights into operational efficiency and customer behavior.
- Improve decision-making by leveraging data-driven insights to identify areas for improvement and optimize business processes.
Other Business Applications
In addition to the above, ERP systems can be integrated with a wide range of other business applications, including:
- Marketing Automation: Automating marketing tasks like email campaigns, social media scheduling, and lead nurturing.
- Project Management: Tracking project progress, managing tasks, and collaborating with team members.
- Document Management: Storing and managing documents electronically, improving efficiency and security.
- Customer Service Portals: Providing customers with self-service options for accessing information and resolving issues.
- Mobile Apps: Enabling employees to access ERP data and perform tasks from their mobile devices.
Integration Methods and Technologies
ERP integration is the process of connecting an ERP system with other business applications to create a seamless flow of data and automate processes. This enables businesses to improve efficiency, reduce errors, and make better decisions. Several methods and technologies are used for ERP integration, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
API Integration
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) are a common and versatile method for integrating ERP systems. They act as intermediaries, allowing different applications to communicate and exchange data securely. APIs define how applications interact, enabling seamless data transfer and automation.
Advantages
- Flexibility and Scalability: APIs offer flexibility, allowing you to integrate with various applications and adapt to changing business needs.
- Real-time Data Exchange: APIs facilitate real-time data exchange, ensuring data consistency and timely access across applications.
- Reduced Development Costs: Using pre-built APIs can significantly reduce development costs and time compared to custom integrations.
Disadvantages
- Complexity: Building and maintaining APIs can be complex, requiring expertise in programming and API management.
- Security Concerns: APIs must be secured to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Limited Functionality: Some APIs may not provide all the necessary functionality for specific integration requirements.
Middleware Integration
Middleware acts as a bridge between the ERP system and other applications, providing a layer of abstraction and facilitating data exchange. It handles data transformation, routing, and protocol conversion, simplifying the integration process.
Advantages
- Simplified Integration: Middleware simplifies integration by providing a standardized interface, reducing the need for custom code.
- Enhanced Data Security: Middleware can enforce security policies and manage data access, ensuring data integrity and confidentiality.
- Improved Performance: Middleware can optimize data flow and improve performance by caching data and managing network traffic.
Disadvantages
- Higher Initial Cost: Implementing middleware can involve higher initial costs compared to APIs.
- Increased Complexity: Managing and maintaining middleware can be complex, requiring specialized expertise.
- Limited Flexibility: Middleware may not be as flexible as APIs, potentially limiting integration options.
Cloud Platform Integration
Cloud platforms provide a comprehensive environment for integrating ERP systems with other applications. They offer pre-built connectors, data synchronization tools, and workflow automation capabilities, simplifying integration and reducing development efforts.
Advantages
- Faster Deployment: Cloud platforms facilitate rapid deployment, reducing the time and resources required for integration.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud platforms offer scalability, allowing you to adjust resources based on your needs, and flexibility, enabling integration with various applications.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Cloud platforms often provide a pay-as-you-go model, reducing upfront costs and offering predictable expenses.
Disadvantages
- Security Concerns: Data security in the cloud can be a concern, requiring careful consideration of cloud provider security measures.
- Vendor Dependence: Reliance on a cloud platform can create vendor lock-in, potentially limiting future integration options.
- Limited Customization: Cloud platforms may offer limited customization options, potentially restricting integration capabilities.
Integration Methods Comparison
| Method | Characteristics | Suitability ||—|—|—|| API Integration | Flexible, scalable, real-time data exchange, reduced development costs | Best for integrating with a wide range of applications, requiring real-time data synchronization, and prioritizing flexibility and scalability. || Middleware Integration | Simplified integration, enhanced data security, improved performance | Ideal for integrating with a limited number of applications, requiring data transformation and security measures, and prioritizing performance and stability.
|| Cloud Platform Integration | Faster deployment, scalability, cost-effectiveness | Suitable for rapid integration, requiring pre-built connectors and workflow automation, and prioritizing speed and affordability. |
Challenges and Considerations for ERP Integration
ERP integration projects, while offering significant benefits, can present various challenges. Successfully navigating these hurdles requires careful planning, effective communication, and a robust understanding of the integration process.
Common Challenges in ERP Integration
This section discusses the common challenges encountered during ERP integration projects.
- Data Migration and Transformation: Migrating data from legacy systems to the new ERP can be complex, requiring thorough data cleansing, transformation, and validation. Inconsistent data formats, missing data points, and duplicate records can pose significant challenges.
- Integration Complexity: Integrating various business applications, including CRM, accounting, supply chain management, and others, can be complex, requiring specialized skills and knowledge. Different systems may have different data structures, APIs, and integration protocols, adding to the complexity.
- User Adoption and Training: A successful ERP integration relies heavily on user adoption. Resistance to change, inadequate training, and lack of user-friendly interfaces can hinder the project’s success.
- Project Management and Communication: Effective project management and communication are crucial for coordinating various stakeholders, managing timelines, and ensuring smooth integration. Poor communication, unclear expectations, and lack of stakeholder buy-in can lead to delays and project failure.
- Customization and Configuration: ERP systems often require customization and configuration to meet specific business needs. This process can be time-consuming and require specialized expertise, potentially impacting project timelines and costs.
- Cost and Time Overruns: ERP integration projects can be expensive and time-consuming. Underestimating the scope, complexity, and resources required can lead to cost and time overruns.
Best Practices for Overcoming Challenges
This section delves into best practices to overcome the challenges associated with ERP integration projects.
- Data Mapping and Cleansing: Thoroughly map data from legacy systems to the new ERP, identifying data inconsistencies, duplicates, and missing information. Cleanse and transform data to ensure accuracy and consistency.
- Phased Integration Approach: Implement integration in phases, starting with critical applications and gradually expanding to other systems. This approach reduces complexity and minimizes disruption to business operations.
- Effective Communication and Training: Communicate the benefits and impact of the integration to all stakeholders, providing regular updates and addressing concerns. Conduct comprehensive training programs to ensure users are comfortable with the new system and its functionalities.
- Robust Project Management: Establish clear project goals, timelines, and milestones. Use project management tools to track progress, identify potential risks, and ensure efficient resource allocation.
- Choose the Right Integration Technologies: Evaluate different integration methods and technologies, such as APIs, middleware, and cloud-based integration platforms, to select the most suitable solution for your organization’s specific needs.
- Seek Expert Assistance: Consider engaging experienced consultants or integration specialists who can provide guidance, expertise, and best practices to ensure successful integration.
Key Considerations for ERP Integration
This section presents key considerations for organizations planning ERP integration projects.
- Business Requirements: Clearly define the business requirements and objectives for the integration project. Identify the key processes, data, and functionalities that need to be integrated.
- Integration Scope: Determine the scope of the integration project, including the systems and applications to be integrated. Prioritize applications based on their criticality and impact on business operations.
- Technology and Infrastructure: Evaluate the existing technology infrastructure and ensure it can support the new ERP system and integration processes. Consider upgrading hardware, software, or network capabilities if necessary.
- Cost and Resources: Develop a realistic budget and allocate sufficient resources for the integration project. Factor in costs for software licenses, implementation services, data migration, training, and ongoing maintenance.
- Change Management: Develop a comprehensive change management plan to address user resistance, provide training, and ensure smooth transition to the new system.
- Vendor Selection: Carefully select an ERP vendor with a proven track record, strong integration capabilities, and a commitment to ongoing support.
- Post-Implementation Support: Plan for post-implementation support, including ongoing maintenance, system upgrades, and user assistance. Ensure a dedicated team is available to address any issues or challenges that may arise.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples

ERP integration projects have yielded significant benefits for businesses across various industries. These integrations have addressed critical business challenges, streamlined operations, and boosted efficiency, ultimately leading to improved profitability and competitive advantage.
Successful ERP Integration Projects
Real-world examples of successful ERP integration projects demonstrate the transformative power of connecting different business applications. These projects have successfully addressed specific business challenges and achieved measurable results.
- Retail Industry: A leading fashion retailer implemented an ERP system to integrate its online and offline operations. The integration enabled real-time inventory visibility, streamlined order fulfillment, and improved customer experience. The retailer saw a 20% increase in sales and a 15% reduction in inventory carrying costs.
- Manufacturing Industry: A global automotive manufacturer integrated its ERP system with its supply chain management (SCM) system. The integration enabled better demand forecasting, optimized production planning, and reduced lead times. The manufacturer achieved a 10% increase in production efficiency and a 5% reduction in inventory levels.
- Healthcare Industry: A large hospital system integrated its ERP system with its electronic health records (EHR) system. The integration enabled improved patient care coordination, reduced administrative burden, and enhanced data analytics capabilities. The hospital system saw a 10% reduction in medical errors and a 5% increase in patient satisfaction.
Benefits of ERP Integration
ERP integration offers numerous benefits for businesses, including:
- Improved Data Visibility: Integration allows businesses to access and analyze data from different systems in a centralized location, providing a holistic view of their operations.
- Streamlined Processes: Integration eliminates data silos and automates workflows, reducing manual processes and improving efficiency.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Integration enables seamless information sharing among different departments, fostering collaboration and improving decision-making.
- Increased Productivity: By automating tasks and eliminating redundancies, integration frees up employees to focus on higher-value activities.
- Reduced Costs: Integration can lead to cost savings by eliminating duplicate data entry, minimizing errors, and optimizing resource allocation.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: Integration enables businesses to provide better customer service by offering personalized experiences and faster response times.
As you embark on your ERP integration journey, remember that careful planning, robust technology selection, and a focus on user adoption are key to success. By embracing the power of integration, you can unlock new levels of efficiency, optimize your business processes, and gain a competitive edge in today’s dynamic marketplace.
General Inquiries: ERP Integration With Other Business Applications
What are the common challenges of ERP integration?
Challenges include data migration complexities, system compatibility issues, user resistance to change, and the potential for integration errors. Addressing these challenges through thorough planning, effective communication, and robust testing is crucial.
How can I ensure successful ERP integration?
Successful integration involves careful planning, clear communication, and a phased implementation approach. It’s also essential to involve key stakeholders, provide comprehensive training, and monitor progress closely.
What are the benefits of integrating ERP with CRM systems?
Integrating ERP with CRM systems provides a holistic view of customer interactions, enabling personalized marketing campaigns, improved customer service, and enhanced sales opportunities.