ERP implementation costs and ROI are critical factors for any organization considering this significant investment. While the initial costs can be substantial, a well-planned and executed ERP implementation can yield substantial returns in the form of increased efficiency, reduced costs, and improved customer satisfaction. This guide delves into the key aspects of ERP implementation costs and ROI, providing insights into cost components, ROI measurement, best practices for cost optimization, and real-world case studies of successful implementations.
Understanding the cost components of an ERP implementation is essential for budgeting and planning. Key factors include software licenses, hardware, consulting fees, training, data migration, and ongoing maintenance. The costs can vary significantly based on the size and complexity of the organization, the chosen ERP solution, and the scope of the implementation project. However, by carefully considering these cost factors and implementing best practices for cost optimization, organizations can minimize expenses and maximize the return on their investment.
Understanding ERP Implementation Costs

ERP implementation costs can be significant, and understanding these costs is crucial for any organization considering an ERP system. A well-planned ERP implementation can yield significant returns on investment, but failing to account for all costs can lead to budget overruns and project delays.
Software Licenses
Software licenses are a major cost component of ERP implementation. The cost of ERP software licenses varies depending on the vendor, the number of users, and the modules included. Some vendors offer tiered pricing structures based on the number of users or the features included. For example, a basic ERP system for a small business might cost a few thousand dollars per year, while a large enterprise-grade system could cost millions of dollars.
- Cloud-based ERP systems: Cloud-based ERP systems are typically offered on a subscription basis, with monthly or annual fees based on the number of users and features. This model can be more cost-effective than traditional on-premises deployments, as it eliminates the need for hardware and software maintenance.
- On-premises ERP systems: On-premises ERP systems require a one-time purchase of software licenses, which can be significantly more expensive than cloud-based solutions. However, this model offers greater control over data security and customization.
Hardware
Hardware costs can be significant, especially for on-premises ERP deployments. These costs include servers, workstations, network equipment, and other hardware components. Cloud-based ERP systems typically eliminate the need for hardware purchases, as the vendor manages the infrastructure.
Consulting Fees
Consulting fees can be a significant cost component of ERP implementation. Consultants provide expertise in selecting, implementing, and customizing ERP systems. The cost of consulting fees varies depending on the consultant’s experience, the complexity of the project, and the size of the organization.
Training
Training is essential to ensure users can effectively use the new ERP system. Training costs can include instructor-led training, online courses, and documentation. The cost of training varies depending on the size of the organization, the complexity of the system, and the training methods used.
Data Migration
Data migration is the process of transferring data from existing systems to the new ERP system. This can be a complex and time-consuming process, requiring specialized skills and tools. Data migration costs can vary depending on the size and complexity of the data, the number of systems involved, and the level of customization required.
Ongoing Maintenance
Ongoing maintenance is essential to keep the ERP system running smoothly and securely. Maintenance costs can include software updates, bug fixes, and technical support. The cost of ongoing maintenance varies depending on the vendor, the size of the organization, and the level of support required.
Factors Influencing ERP Implementation Costs
Several factors can influence the total cost of an ERP implementation.
- Company size: Larger companies typically have more complex business processes and require more extensive ERP systems. This can lead to higher software licensing costs, consulting fees, and training costs.
- Industry complexity: Some industries have more complex regulations and compliance requirements than others. This can lead to higher implementation costs, as the ERP system must be customized to meet these requirements.
- Project scope: The scope of the project can significantly impact the cost of implementation. Projects that involve integrating multiple systems or implementing a wide range of modules will typically be more expensive than projects with a narrow scope.
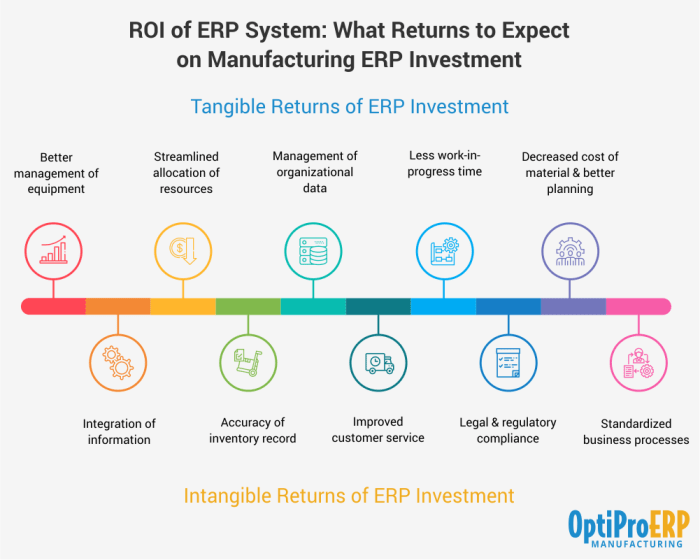
Quantifying the Return on Investment (ROI)

Determining the return on investment (ROI) of an ERP implementation is crucial for justifying the expenditure and demonstrating its value to stakeholders. While the initial costs are readily apparent, the benefits are often intangible and challenging to quantify. This section delves into key metrics for measuring ROI, strategies for tracking and quantifying benefits, and the challenges involved in accurately assessing the return on investment.
Identifying Key Metrics for Measuring ROI
Key metrics for measuring the ROI of an ERP implementation can be categorized into various areas, including:
- Increased Efficiency: This can be measured through reduced processing times, improved inventory management, and faster order fulfillment. For example, tracking the reduction in time taken to process an order or the decrease in inventory holding costs can demonstrate the efficiency gains achieved.
- Reduced Costs: ERP implementations can lead to significant cost savings through automation, streamlined processes, and reduced errors. Examples include quantifying the reduction in labor costs due to automation, the decrease in manual data entry errors, or the savings from optimized procurement processes.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: This can be measured through increased customer retention rates, higher satisfaction scores, and improved response times. Tracking metrics like customer satisfaction surveys, net promoter scores, and order fulfillment times can demonstrate the impact of ERP on customer experience.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: ERP systems provide real-time data and analytics, enabling better informed decisions. This can be measured by tracking improvements in forecasting accuracy, inventory management, and supply chain planning. For instance, analyzing the accuracy of sales forecasts before and after the ERP implementation can highlight the impact on decision-making.
Tracking and Quantifying the Benefits
To demonstrate the ROI of an ERP implementation, businesses need to track and quantify the benefits achieved. This can be done through:
- Establishing Baselines: Before implementing ERP, establish baseline metrics for key performance indicators (KPIs) such as order processing time, inventory turnover rate, and customer satisfaction scores. This provides a benchmark for measuring improvements after the implementation.
- Monitoring and Reporting: Regularly monitor the KPIs after the ERP implementation and report on the changes observed. This data can be used to demonstrate the impact of the ERP system on key business processes.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Conduct a cost-benefit analysis to compare the initial investment in the ERP system with the savings and benefits realized. This analysis can help quantify the ROI and justify the investment.
- Case Studies and Testimonials: Share success stories and testimonials from employees and customers who have benefited from the ERP implementation. These qualitative data points can provide valuable insights into the impact of the system.
Challenges in Measuring ROI
Accurately measuring the ROI of an ERP implementation can be challenging due to:
- Intangible Benefits: Some benefits of ERP, such as improved decision-making and enhanced employee morale, are intangible and difficult to quantify. This makes it challenging to fully capture the value of the implementation.
- Data Availability and Accuracy: Accessing accurate and reliable data for measuring ROI can be difficult, especially in organizations with legacy systems or fragmented data sources. This can hinder the ability to track progress and quantify benefits.
- Time Lag: It can take time for the full benefits of an ERP implementation to materialize. This makes it challenging to measure the ROI immediately after the implementation and requires patience and consistent monitoring.
- External Factors: External factors such as economic fluctuations or industry changes can influence business performance and make it difficult to isolate the impact of the ERP implementation on ROI.
Strategies for Overcoming Challenges
To overcome the challenges in measuring ROI, businesses can implement the following strategies:
- Focus on Key Metrics: Prioritize tracking and quantifying the most important metrics that align with business goals and demonstrate the impact of the ERP implementation.
- Data Integration and Standardization: Ensure data consistency and accuracy by integrating data from different sources and standardizing data definitions across the organization.
- Regular Monitoring and Reporting: Regularly monitor and report on key performance indicators to track progress and identify areas for improvement.
- Collaboration with Stakeholders: Involve key stakeholders in the ROI measurement process to ensure alignment on metrics and reporting methodologies.
- Qualitative Data Collection: Complement quantitative data with qualitative data, such as employee feedback and customer testimonials, to gain a comprehensive understanding of the impact of the ERP implementation.
ERP Implementation Best Practices for Cost Optimization
Optimizing ERP implementation costs is crucial for maximizing ROI. This involves a strategic approach to planning, communication, resource allocation, and vendor negotiations. Implementing these best practices can significantly reduce expenses and ensure a successful project.
Thorough Planning and Preparation, ERP implementation costs and ROI
Effective planning is the foundation of a successful ERP implementation. A well-defined plan minimizes unforeseen costs and delays.
- Define Clear Project Scope: A clear project scope Artikels the specific functionalities and modules to be implemented. This helps in determining the required resources and budget.
- Develop a Detailed Implementation Roadmap: A comprehensive roadmap with timelines, milestones, and deliverables provides a structured approach to the project. It helps in identifying potential cost-saving opportunities and mitigating risks.
- Conduct a Thorough Gap Analysis: This analysis identifies the differences between current processes and the desired functionalities of the new ERP system. It helps in customizing the implementation to meet specific business needs, reducing unnecessary costs.
- Establish Realistic Expectations: Setting realistic expectations for the implementation process and the impact of the new system helps in managing costs effectively.
Effective Communication and Collaboration
Open and effective communication throughout the implementation process is essential for cost optimization.
- Establish a Strong Communication Plan: Regular communication between stakeholders, including project team members, management, and end-users, ensures everyone is informed and aligned. It helps in addressing issues promptly and minimizing rework, which can significantly impact costs.
- Encourage Active User Involvement: Engaging end-users in the implementation process helps in identifying potential cost-saving opportunities and ensuring the system meets their specific needs.
- Provide Training and Support: Adequate training for end-users on the new system helps in reducing support costs and ensuring the system is used effectively.
Efficient Resource Allocation
Proper resource allocation is crucial for minimizing implementation costs.
- Leverage Internal Expertise: Utilizing existing internal expertise can significantly reduce implementation costs. Identifying and leveraging internal resources with relevant skills and experience can reduce reliance on external consultants.
- Strategic Outsourcing: Outsourcing specific tasks, such as data migration or system integration, to specialized vendors can be cost-effective. It allows the organization to focus on core competencies while leveraging the expertise of external specialists.
- Manage Project Team Size: Optimizing the size of the project team based on the scope and complexity of the implementation ensures efficient resource utilization and minimizes costs.
Negotiating Favorable Pricing with ERP Vendors
Negotiating favorable pricing with ERP vendors is essential for cost optimization.
- Compare Vendor Offerings: Evaluating different vendor offerings allows organizations to compare pricing models, functionalities, and support services. This enables them to negotiate the best possible deal.
- Leverage Existing Infrastructure: Organizations can leverage existing infrastructure, such as hardware, software, or network connectivity, to reduce implementation costs. This can be achieved by negotiating favorable terms with vendors who can utilize existing resources.
- Explore Alternative Pricing Models: Exploring alternative pricing models, such as subscription-based or cloud-based solutions, can provide more cost-effective options compared to traditional licensing models.
Aligning ERP Implementation with Business Objectives
Aligning the ERP implementation project with business objectives is crucial for ensuring a positive ROI.
- Identify Key Business Goals: Defining clear business objectives for the ERP implementation helps in selecting the appropriate functionalities and modules. This ensures the system aligns with the organization’s strategic priorities and contributes to achieving its goals.
- Measure and Track Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) related to business objectives helps in evaluating the effectiveness of the ERP implementation and identifying areas for improvement. This ensures the system is delivering the desired results and contributing to the organization’s overall success.
Case Studies: ERP Implementation Costs And ROI
Real-world examples demonstrate the potential of ERP implementations to drive business growth and improve operational efficiency. By examining successful ERP implementations, we can gain valuable insights into the strategies and approaches that contribute to a high ROI.
ERP Implementation Success Stories
These case studies highlight the diverse benefits of ERP implementation across various industries.
| Company | Industry | Implementation Challenges | Achieved ROI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Walmart | Retail | Integrating data from multiple systems, managing a global supply chain, and ensuring data security. | Improved inventory management, reduced costs, and enhanced customer service. |
| General Electric | Manufacturing | Standardizing processes across multiple business units, managing complex data, and ensuring seamless integration with existing systems. | Increased productivity, improved efficiency, and enhanced decision-making capabilities. |
| Nike | Apparel & Footwear | Managing global supply chains, tracking inventory levels, and optimizing production processes. | Reduced lead times, improved inventory accuracy, and increased sales. |
| Starbucks | Food & Beverage | Managing complex operations, streamlining ordering processes, and enhancing customer experience. | Improved operational efficiency, increased customer satisfaction, and enhanced brand loyalty. |
Ultimately, the success of an ERP implementation hinges on a clear understanding of the costs involved, the potential benefits, and the strategies for achieving a positive ROI. By carefully planning, executing, and measuring the results, organizations can leverage ERP technology to streamline operations, improve decision-making, and gain a competitive edge in the marketplace. This guide has provided a framework for navigating the complexities of ERP implementation costs and ROI, empowering organizations to make informed decisions and achieve their desired business outcomes.
Common Queries
What are the biggest challenges in measuring ERP implementation ROI?
Accurately measuring the ROI of an ERP implementation can be challenging due to factors like intangible benefits, difficulty in isolating the impact of the ERP system, and the need for robust data collection and analysis.
How can I negotiate favorable pricing with ERP vendors?
Thorough research, understanding your specific needs, comparing vendor offerings, and leveraging your bargaining power through factors like project size and long-term commitment can help you negotiate favorable pricing.
What are some examples of successful ERP implementation case studies?
Case studies from companies like Walmart, Amazon, and Netflix showcase the transformative power of ERP implementations in driving efficiency, cost savings, and improved customer experiences.