ERP for educational institutions is revolutionizing the way schools, colleges, and universities operate. By integrating various administrative, financial, and academic processes, ERP systems provide a comprehensive platform for managing all aspects of an institution’s operations.
From student enrollment and financial aid to faculty scheduling and resource allocation, ERP systems streamline workflows, enhance efficiency, and improve decision-making. By centralizing data and providing real-time insights, ERP systems empower educational institutions to optimize their resources, improve student outcomes, and create a more engaging learning environment.
Introduction to ERP for Educational Institutions
An Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system is a comprehensive software solution designed to manage and integrate all the core business processes of an organization. For educational institutions, ERP systems offer a centralized platform to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and enhance the overall learning experience. ERP systems can be tailored to meet the specific needs of educational institutions, providing a single source of truth for all data and processes.
This integration enables seamless information flow across departments, leading to better decision-making and a more collaborative environment.
Examples of ERP System Applications in Educational Institutions, ERP for educational institutions
ERP systems can be implemented in various aspects of an educational institution, including:
- Student Management: From enrollment and admissions to course registration, attendance tracking, and grade management, ERP systems provide a robust platform for managing student data and interactions.
- Faculty and Staff Management: ERP systems streamline payroll, benefits administration, and performance evaluations for faculty and staff, improving efficiency and employee satisfaction.
- Financial Management: ERP systems provide tools for budgeting, accounting, and financial reporting, enabling institutions to manage their finances effectively and ensure financial transparency.
- Resource Management: ERP systems facilitate the management of resources such as classrooms, laboratories, and equipment, optimizing utilization and minimizing conflicts.
- Communication and Collaboration: ERP systems offer integrated communication tools, such as email, messaging, and online forums, fostering collaboration between students, faculty, and staff.
Benefits of Implementing an ERP System
The implementation of an ERP system can bring numerous benefits to educational institutions, including:
- Improved Operational Efficiency: ERP systems automate repetitive tasks, reducing manual work and freeing up staff time for more strategic initiatives.
- Enhanced Data Visibility and Reporting: Centralized data management provides real-time insights into key performance indicators, enabling data-driven decision-making.
- Improved Communication and Collaboration: Integrated communication tools facilitate seamless information flow and collaboration between stakeholders.
- Reduced Costs: Streamlined processes and improved efficiency can lead to significant cost savings for educational institutions.
- Enhanced Student Experience: ERP systems can provide students with personalized access to information, services, and resources, enhancing their overall learning experience.
Key Features of ERP for Educational Institutions
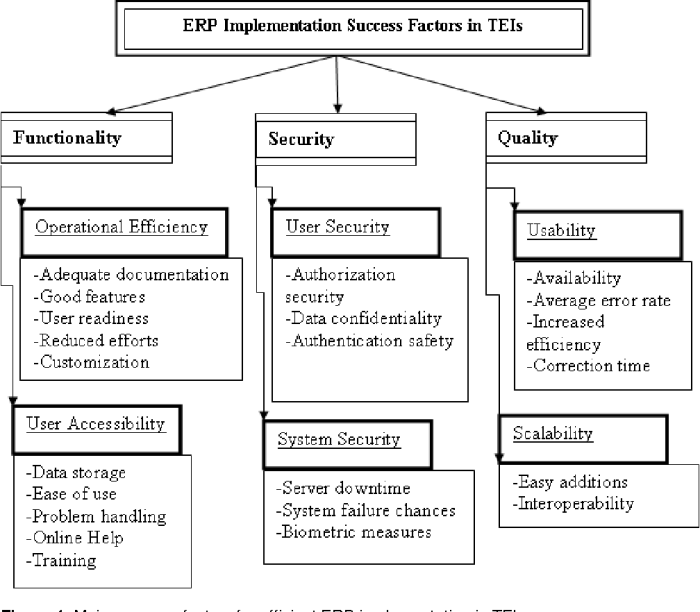
ERP systems, designed specifically for educational institutions, offer a comprehensive suite of features that streamline administrative processes, enhance academic operations, and improve overall efficiency. These systems integrate various departments and functions, providing a centralized platform for managing data, automating tasks, and fostering collaboration.
Core Functionalities of ERP for Educational Institutions
ERP systems for educational institutions encompass a range of functionalities that cater to the specific needs of this sector. These features streamline administrative tasks, enhance academic operations, and facilitate effective communication and collaboration.
| Feature Name | Description | Benefits for Educational Institutions | Examples of Implementation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Student Information Management (SIM) | Manages student data, including personal details, academic records, attendance, and financial information. | Centralized student data, improved record-keeping, enhanced reporting, and personalized learning experiences. | Tracking student progress, generating transcripts, managing enrollment, and providing personalized learning resources. |
| Financial Management | Handles financial transactions, budgeting, accounting, and reporting. | Improved financial transparency, efficient budgeting, accurate accounting, and streamlined payment processing. | Managing tuition fees, payroll, scholarships, and financial aid. |
| Human Resources Management (HRM) | Manages employee information, payroll, benefits, and performance evaluations. | Improved employee engagement, efficient payroll processing, and streamlined HR processes. | Managing employee records, scheduling, training, and performance reviews. |
| Academic Management | Supports academic processes, including course scheduling, curriculum management, and grading. | Improved academic planning, efficient course scheduling, and effective student assessment. | Managing course catalogs, creating schedules, assigning grades, and generating reports. |
| Admissions Management | Facilitates the application, admission, and enrollment processes for prospective students. | Simplified admissions process, increased enrollment rates, and enhanced communication with applicants. | Managing application forms, processing applications, and tracking applicant progress. |
| Library Management | Manages library resources, including books, journals, and digital content. | Improved library operations, enhanced access to resources, and streamlined information retrieval. | Cataloging library materials, managing circulation, and providing online access to resources. |
| Reporting and Analytics | Provides comprehensive reports and dashboards for data analysis and decision-making. | Data-driven decision-making, improved performance tracking, and enhanced accountability. | Generating reports on student performance, financial status, and operational efficiency. |
| Communication and Collaboration | Facilitates communication and collaboration among students, faculty, staff, and parents. | Improved communication channels, enhanced collaboration, and increased engagement. | Using online forums, messaging platforms, and virtual classrooms for communication and collaboration. |
Modules in ERP for Educational Institutions
An ERP system for educational institutions is typically composed of various modules, each designed to manage specific aspects of the institution’s operations. These modules work in tandem to provide a comprehensive and integrated approach to managing the institution’s resources, processes, and information.
Student Information Management
This module is the core of an educational ERP system, storing and managing all student-related data. It acts as a central repository for information such as:
- Student demographics (name, address, contact information)
- Academic records (courses, grades, attendance)
- Financial information (fees, scholarships, payments)
- Extracurricular activities and achievements
This module facilitates various processes, including:
- Student admissions and enrollment
- Course registration and scheduling
- Grade management and reporting
- Fee collection and payment processing
- Student communication and notifications
By centralizing student data, this module enables efficient student management, streamlined communication, and improved decision-making based on accurate and readily available information. For instance, an institution can use this module to generate reports on student performance, identify trends, and implement targeted interventions to improve student success.
Faculty and Staff Management
This module focuses on managing faculty and staff information, including their:
- Personal details (name, contact information, qualifications)
- Employment details (position, salary, benefits)
- Teaching assignments and schedules
- Performance evaluations and professional development
The module facilitates tasks like:
- Faculty recruitment and onboarding
- Payroll and benefits administration
- Time and attendance tracking
- Performance management and development
- Communication and collaboration among faculty and staff
This module enables institutions to streamline HR processes, ensure compliance with labor regulations, and improve faculty and staff engagement. For example, an institution can use this module to automate payroll calculations, track employee performance, and provide timely professional development opportunities.
Financial Management
This module handles the institution’s financial operations, including:
- Budgeting and financial planning
- Fee collection and accounting
- Inventory management (for supplies and equipment)
- Financial reporting and analysis
The module supports:
- Generating financial statements and reports
- Managing accounts payable and receivable
- Tracking expenses and revenues
- Auditing and compliance with financial regulations
This module helps institutions maintain financial stability, make informed financial decisions, and ensure transparency in financial operations. For example, an institution can use this module to track expenses against budget, identify areas of potential savings, and generate reports for stakeholders.
Academic Management
This module focuses on managing the academic aspects of the institution, including:
- Course catalog and curriculum management
- Timetable and scheduling
- Exam management and grading
- Research and publication management
The module enables:
- Creating and managing course syllabuses
- Scheduling classes and exams
- Generating academic transcripts and reports
- Managing research projects and publications
This module helps institutions ensure academic quality, streamline academic processes, and facilitate effective academic administration. For instance, an institution can use this module to create a comprehensive course catalog, schedule classes efficiently, and generate reports on student academic performance.
Library Management
This module manages the institution’s library resources, including:
- Cataloging and indexing books, journals, and other materials
- Circulation and loan management
- Resource acquisition and procurement
- Digital library management
The module facilitates:
- Searching and accessing library resources
- Managing library membership and borrowing privileges
- Tracking library inventory and usage
- Providing online access to digital resources
This module ensures efficient library operations, improves access to information for students and faculty, and supports research and learning activities. For example, an institution can use this module to create a searchable online library catalog, manage digital resources, and track library usage statistics.
Admissions and Recruitment
This module manages the admissions and recruitment process, including:
- Application processing and evaluation
- Admissions decisions and notifications
- Marketing and outreach activities
- Tracking applicant data and statistics
The module enables:
- Creating and managing application forms
- Automating application evaluation processes
- Sending admission decisions and notifications
- Analyzing applicant data to improve recruitment strategies
This module helps institutions streamline the admissions process, attract qualified applicants, and make informed admissions decisions. For instance, an institution can use this module to track application trends, identify potential areas for improvement in recruitment efforts, and generate reports on admissions outcomes.
Alumni Management
This module focuses on managing relationships with alumni, including:
- Alumni database management
- Communication and engagement activities
- Fundraising and development efforts
- Alumni career services
The module enables:
- Maintaining an up-to-date alumni database
- Sending newsletters and updates to alumni
- Organizing alumni events and reunions
- Facilitating networking opportunities for alumni
This module helps institutions cultivate strong relationships with alumni, foster a sense of community, and leverage alumni networks for fundraising, recruitment, and other institutional initiatives. For example, an institution can use this module to track alumni career paths, identify successful alumni who can serve as mentors, and organize alumni events to promote engagement.
Other Modules
In addition to the core modules mentioned above, educational ERP systems may include specialized modules tailored to specific needs, such as:
- Hostel Management: Manages hostel bookings, room assignments, and related services.
- Transportation Management: Manages school buses and transportation services.
- Inventory Management: Tracks and manages inventory of supplies and equipment.
- Event Management: Organizes and manages institutional events and conferences.
- Learning Management System (LMS): Provides online learning platforms and resources.
These modules can be customized to meet the specific requirements of different institutions, ensuring that the ERP system provides a comprehensive solution for managing all aspects of institutional operations.
Challenges of Implementing ERP in Educational Institutions
Implementing an ERP system in an educational institution can be a complex and challenging undertaking. While ERP systems offer numerous benefits, successful implementation requires careful planning, effective communication, and a comprehensive approach to address potential roadblocks.
Resistance to Change
Resistance to change is a common hurdle in any organizational transformation, particularly in educational institutions, which often have established routines and processes.
- Fear of the Unknown: Faculty, staff, and students may be apprehensive about the changes that an ERP system will bring, particularly if they are unfamiliar with the technology or its implications.
- Concerns about Job Security: Some individuals may worry that the new system will automate their tasks, leading to job losses or changes in responsibilities.
- Disruption to Existing Workflows: The implementation of an ERP system can disrupt existing workflows and require individuals to adapt to new processes, which can be frustrating and time-consuming.
Strategies for Overcoming Resistance to Change:
- Communicate Effectively: Provide clear and consistent communication about the benefits of the ERP system, its impact on individual roles, and the implementation timeline.
- Involve Stakeholders: Engage key stakeholders, including faculty, staff, and students, in the planning and implementation process to ensure their voices are heard and concerns are addressed.
- Provide Training and Support: Offer comprehensive training programs to familiarize users with the new system and provide ongoing support to address any questions or challenges they may encounter.
- Demonstrate Success: Highlight early successes of the ERP system to build confidence and demonstrate its value to the institution.
Data Migration and Integration
Migrating data from existing systems and integrating it into the new ERP system can be a complex and time-consuming process.
- Data Accuracy and Consistency: Ensuring the accuracy and consistency of data during migration is crucial to avoid errors and maintain data integrity in the ERP system.
- Data Format Compatibility: Different systems may use different data formats, which can create challenges in migrating and integrating data.
- Data Security and Privacy: Data security and privacy are paramount concerns during data migration. Institutions must ensure that sensitive data is protected and handled in accordance with relevant regulations.
Strategies for Overcoming Data Migration and Integration Challenges:
- Thorough Data Mapping: Carefully map existing data fields to the corresponding fields in the ERP system to ensure accurate and consistent data transfer.
- Data Cleansing and Validation: Cleanse and validate existing data to eliminate errors and inconsistencies before migrating it to the ERP system.
- Phased Migration: Migrate data in phases to minimize disruption and allow for testing and validation of the data in the ERP system.
- Data Security Measures: Implement robust data security measures, such as encryption and access controls, to protect sensitive data during migration and integration.
System Customization and Configuration
Educational institutions often have unique requirements and processes that may not be fully supported by standard ERP systems.
- Customizations: The need for customizations can increase the complexity and cost of implementation, as well as potential maintenance issues in the future.
- Configuration Complexity: Configuring the ERP system to meet specific institutional needs can be a challenging and time-consuming process, requiring expertise in both the ERP system and the institution’s processes.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Integrating the ERP system with existing systems, such as student information systems (SIS) or financial management systems, can be complex and require careful planning and coordination.
Strategies for Overcoming System Customization and Configuration Challenges:
- Prioritize Requirements: Carefully identify and prioritize the most critical requirements for the ERP system to minimize the need for extensive customizations.
- Leverage Pre-Built Functionality: Explore the pre-built functionality of the ERP system and leverage existing modules to meet as many requirements as possible.
- Engage Experienced Consultants: Engage experienced ERP consultants who have expertise in both the ERP system and the education sector to assist with configuration and integration.
- Testing and Validation: Conduct thorough testing and validation of the customized and configured system to ensure it meets the institution’s specific needs and performs as expected.
Training and Support
Providing adequate training and ongoing support to users is crucial for the successful adoption and utilization of the ERP system.
- User Training: Comprehensive training programs are essential to familiarize users with the new system, its features, and how to perform their tasks effectively.
- Support Resources: Providing access to readily available support resources, such as online documentation, FAQs, and help desk support, is essential for users to resolve issues and get assistance when needed.
- Change Management: Ongoing change management initiatives are necessary to keep users informed about updates, enhancements, and new features of the ERP system.
Strategies for Overcoming Training and Support Challenges:
- Tailored Training Programs: Develop training programs that are tailored to the specific needs and roles of different user groups, such as faculty, staff, and students.
- Multiple Training Formats: Offer training in various formats, such as online courses, workshops, and one-on-one sessions, to cater to different learning styles and preferences.
- User-Friendly Documentation: Create clear and concise user documentation that is easily accessible and searchable.
- Responsive Support: Establish a responsive help desk or support team to address user inquiries and resolve issues promptly.
Cost and Return on Investment
The cost of implementing an ERP system can be significant, and institutions need to carefully consider the return on investment (ROI) before making a decision.
- Implementation Costs: Implementation costs can include software licenses, hardware upgrades, consulting fees, data migration, training, and ongoing maintenance.
- Operational Efficiency: ERP systems can improve operational efficiency by streamlining processes, reducing manual tasks, and automating workflows, leading to cost savings.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: ERP systems provide access to real-time data and insights, enabling institutions to make data-driven decisions and optimize resource allocation.
Strategies for Overcoming Cost and Return on Investment Challenges:
- Develop a Comprehensive Business Case: Create a detailed business case that Artikels the projected costs and benefits of the ERP system, including potential cost savings, increased efficiency, and improved decision-making.
- Explore Funding Options: Explore various funding options, such as grants, loans, or internal budget allocations, to finance the implementation costs.
- Prioritize High-Impact Modules: Focus on implementing high-impact modules that deliver significant benefits and ROI early on, such as financial management, student information, or human resources.
- Measure and Track ROI: Regularly measure and track the ROI of the ERP system to assess its impact on operational efficiency, cost savings, and other key performance indicators.
Choosing the Right ERP System for Educational Institutions: ERP For Educational Institutions

Selecting the right ERP system is a critical decision for educational institutions. A well-chosen ERP can streamline operations, improve efficiency, and enhance the overall student experience. However, choosing the wrong system can lead to costly implementation, integration issues, and ultimately, a less effective solution. Therefore, a thorough evaluation process is essential.
Factors to Consider When Selecting an ERP System
Educational institutions need to consider several factors when selecting an ERP system. These factors should be aligned with the institution’s specific needs, goals, and resources.
- Institutional Size and Complexity: The size and complexity of the institution are key factors. Large universities with multiple campuses and diverse programs will require a more robust and scalable ERP system than smaller institutions.
- Academic Programs and Structure: The specific academic programs and structure of the institution should be considered. An ERP system should be able to handle the unique requirements of different academic departments, such as registration, course scheduling, and faculty workload management.
- Student Demographics and Needs: Understanding the student demographics and needs is crucial. For example, institutions with a large international student population may require an ERP system with multilingual capabilities and support for different currency formats.
- Budget and Resources: Budget constraints and available resources will influence the selection process. Institutions should consider the initial implementation cost, ongoing maintenance fees, and the cost of training staff on the new system.
Criteria for Evaluating ERP Solutions
Once the key factors are identified, educational institutions can evaluate different ERP solutions based on specific criteria.
- Functionality and Features: The ERP system should offer a comprehensive set of features that meet the institution’s specific needs. This includes modules for student information management, financial management, human resources, and academic program management.
- Scalability and Flexibility: The system should be scalable to accommodate future growth and changes in the institution’s needs. Flexibility is also crucial, allowing the institution to customize the system to its unique requirements.
- Cost and Budget: The cost of the ERP system, including implementation, training, and ongoing maintenance, should be carefully considered. Institutions should evaluate different pricing models, such as subscription-based or perpetual licenses, and ensure the cost fits within the institution’s budget.
- Vendor Reputation and Support: The vendor’s reputation and support services are critical factors. Institutions should choose a vendor with a proven track record of successful implementations in educational institutions and a strong commitment to customer support.
- Integration with Existing Systems: The ERP system should integrate seamlessly with existing systems, such as learning management systems (LMS), financial accounting software, and other critical applications. This ensures data consistency and avoids data silos.
Best Practices for Choosing an ERP System
Choosing the right ERP system is a complex process that requires careful planning and execution. The following best practices can help institutions make informed decisions:
- Form a Selection Committee: Establish a committee composed of key stakeholders from different departments, including IT, finance, academics, and administration. This ensures a diverse perspective and a comprehensive evaluation.
- Define Clear Requirements: Develop a detailed list of requirements that Artikels the specific needs and functionalities of the ERP system. This will help narrow down the search and evaluate vendors based on their ability to meet those requirements.
- Conduct a Thorough Vendor Evaluation: Carefully evaluate potential vendors based on the criteria Artikeld above. Request demos, conduct site visits, and speak with other institutions that have implemented the vendor’s ERP system.
- Negotiate a Strong Contract: Before signing a contract, carefully review all terms and conditions, including pricing, implementation timeline, support services, and data ownership. Negotiate favorable terms that protect the institution’s interests.
- Plan for Implementation: Develop a comprehensive implementation plan that includes training, data migration, and ongoing support. This will ensure a smooth transition to the new system and minimize disruption to daily operations.
Successful Implementation of ERP in Educational Institutions

Successfully implementing an ERP system in an educational institution requires careful planning, stakeholder engagement, and a clear understanding of the institution’s specific needs. Numerous institutions have successfully adopted ERP systems, reaping significant benefits in terms of efficiency, transparency, and improved decision-making.
Examples of Successful ERP Implementations in Educational Institutions
The success of ERP implementation in educational institutions is evident in numerous case studies. Here are a few examples:
- University of California, Berkeley: The University of California, Berkeley, implemented an ERP system to streamline its administrative processes, improve financial management, and enhance student services. The implementation resulted in significant cost savings, increased efficiency, and improved student satisfaction.
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT): MIT implemented an ERP system to manage its complex research activities, financial operations, and student enrollment. The system helped the institution optimize resource allocation, improve data accuracy, and enhance decision-making capabilities.
- University of Oxford: The University of Oxford implemented an ERP system to manage its vast research portfolio, financial operations, and human resources. The system enabled the university to improve data visibility, enhance collaboration among researchers, and streamline administrative processes.
Case Studies Highlighting Benefits and Outcomes
- Case Study: XYZ University
- Challenge: XYZ University was facing challenges with manual processes, data silos, and inefficiencies in administrative tasks. The institution was struggling to provide timely and accurate information to stakeholders, leading to delays and frustration.
- Solution: XYZ University implemented an ERP system to automate key processes, integrate data across different departments, and improve communication and collaboration.
- Outcome: The ERP implementation resulted in a significant reduction in manual work, improved data accuracy, and enhanced transparency. The institution was able to provide timely and accurate information to stakeholders, leading to improved decision-making and increased efficiency.
- Case Study: ABC College
- Challenge: ABC College was struggling with managing its student records, financial transactions, and human resources processes manually. The institution was facing challenges with data accuracy, compliance, and reporting.
- Solution: ABC College implemented an ERP system to automate its administrative processes, improve data accuracy, and enhance reporting capabilities.
- Outcome: The ERP implementation resulted in improved data accuracy, enhanced compliance with regulations, and improved reporting capabilities. The institution was able to streamline its administrative processes, reduce errors, and make better-informed decisions.
Key Factors Contributing to Successful ERP Implementations
Several key factors contribute to the success of ERP implementations in educational institutions. These factors include:
- Clear Vision and Objectives: A clear understanding of the institution’s goals and objectives for the ERP implementation is crucial. The institution should define the specific problems it seeks to solve and the desired outcomes.
- Strong Leadership and Sponsorship: Strong leadership and sponsorship from senior management are essential for the success of any ERP implementation. Leaders should champion the project, provide necessary resources, and ensure alignment with the institution’s overall strategic goals.
- Effective Communication and Stakeholder Engagement: Open and effective communication with all stakeholders, including faculty, staff, students, and parents, is essential for a successful ERP implementation. Stakeholders should be informed about the project’s goals, timelines, and potential impacts.
- Proper Planning and Execution: A well-defined implementation plan with clear timelines, milestones, and responsibilities is essential. The plan should address all aspects of the implementation, including data migration, system configuration, training, and change management.
- Adequate Resources and Training: The institution should allocate sufficient resources, including budget, staff, and time, for the ERP implementation. Adequate training for users is crucial to ensure successful adoption and utilization of the system.
- Change Management and User Adoption: Implementing an ERP system involves significant changes in processes and workflows. Effective change management strategies are crucial to ensure smooth transition and user adoption.
- Ongoing Support and Maintenance: The ERP implementation should be followed by ongoing support and maintenance to ensure the system remains functional and meets the institution’s evolving needs.
Future Trends in ERP for Educational Institutions
The world of education is rapidly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing student expectations. ERP systems are at the forefront of this transformation, continually adapting to meet the evolving needs of educational institutions. As we look ahead, several emerging trends in ERP technology are poised to significantly impact how educational institutions operate and deliver their services.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are transforming various industries, and education is no exception. These technologies are poised to revolutionize how ERP systems operate in educational institutions.
- Personalized Learning Experiences: AI-powered systems can analyze student data, including academic performance, learning styles, and interests, to create personalized learning paths. This allows for tailored instruction and resources that cater to individual needs, enhancing student engagement and outcomes.
- Automated Processes: AI and ML can automate repetitive tasks such as scheduling, grading, and administrative processes, freeing up educators’ time to focus on more strategic activities like student mentorship and curriculum development.
- Predictive Analytics: These technologies can analyze historical data to identify trends and predict future outcomes. Educational institutions can use this information to make data-driven decisions about resource allocation, student support, and program development. For example, an ERP system could predict student dropout rates based on historical data and identify students at risk, allowing interventions to be implemented early on.
Cloud-Based ERP Systems
Cloud computing has become increasingly prevalent in recent years, offering several advantages for educational institutions.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud-based ERP systems can easily scale to accommodate growing student populations and changing needs. This flexibility allows institutions to adapt to evolving demands without investing in expensive hardware upgrades.
- Accessibility and Collaboration: Cloud-based systems are accessible from anywhere with an internet connection, enabling students, faculty, and staff to access information and collaborate on projects remotely. This is particularly important for institutions with geographically dispersed campuses or students studying online.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Cloud-based ERP systems typically have lower upfront costs compared to traditional on-premises systems. They also offer a subscription-based model, allowing institutions to pay for only the resources they need, which can be more cost-effective in the long run.
Integration with Other Educational Technologies
Modern ERP systems are designed to seamlessly integrate with other educational technologies, creating a unified ecosystem for learning and administration.
- Learning Management Systems (LMS): Integrating ERP systems with LMS platforms allows institutions to manage student enrollment, track progress, and deliver online courses within a single system. This streamlined approach enhances efficiency and improves the overall learning experience.
- Student Information Systems (SIS): ERP systems can be integrated with SIS to provide a comprehensive view of student data, including academic records, financial information, and personal details. This integration simplifies administrative tasks and facilitates data-driven decision-making.
- Communication and Collaboration Tools: Integrating ERP systems with communication and collaboration tools, such as video conferencing platforms and instant messaging apps, allows for more effective communication and collaboration among students, faculty, and staff. This can be particularly beneficial for institutions with diverse student populations or those offering online learning programs.
Implementing an ERP system in an educational institution is a significant undertaking, but the potential benefits are substantial. By carefully planning and executing the implementation process, institutions can reap the rewards of improved efficiency, enhanced data-driven decision-making, and a more robust and responsive learning environment. As technology continues to evolve, ERP systems are poised to play an even greater role in shaping the future of education, enabling institutions to adapt to changing demands and deliver a world-class learning experience.
Q&A
What are the key benefits of implementing an ERP system for educational institutions?
ERP systems offer numerous benefits, including improved administrative efficiency, enhanced financial management, streamlined student and faculty management, optimized resource allocation, and better data analysis and reporting capabilities.
How much does it cost to implement an ERP system in an educational institution?
The cost of implementing an ERP system can vary depending on the size and complexity of the institution, the chosen ERP solution, and the scope of the implementation. It’s essential to conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis to determine the financial feasibility of implementing an ERP system.
What are the common challenges faced during ERP implementation in educational institutions?
Challenges include resistance to change, data migration and integration complexities, system customization and configuration requirements, training and support needs, and the cost of implementation and ongoing maintenance.
How can I choose the right ERP system for my educational institution?
Consider factors such as functionality and features, scalability and flexibility, cost and budget, vendor reputation and support, and integration with existing systems. It’s crucial to select an ERP system that aligns with the institution’s specific needs and long-term goals.