ERP software for retail businesses with multiple locations is a game-changer, tackling the complexities of managing inventory, sales, and customer data across diverse locations. Imagine a system that unites your stores, providing real-time insights into stock levels, sales performance, and customer preferences, all in one centralized platform. This is the power of ERP, empowering retail businesses to optimize operations, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction.
By implementing an ERP system, retail businesses can gain a comprehensive view of their operations, allowing for informed decision-making and proactive adjustments. From streamlining inventory management to optimizing supply chains and improving customer service, ERP software empowers multi-location retail businesses to achieve greater efficiency and profitability.
Choosing the Right ERP Software for Your Retail Business

Implementing an ERP system can be a game-changer for multi-location retail businesses, streamlining operations, enhancing efficiency, and providing valuable insights. However, choosing the right ERP software is crucial to ensure a successful implementation and maximize its benefits.
Factors to Consider When Selecting an ERP System
The selection process involves evaluating various factors that align with your specific business needs and goals. This includes considering your business size, industry-specific needs, budget, and integration capabilities.
- Business Size: The size of your retail operation plays a significant role in determining the complexity and scalability of the ERP system you require. Small businesses may find basic solutions sufficient, while larger enterprises may need more robust and feature-rich systems.
- Industry-Specific Needs: Different retail industries have unique requirements. For example, fashion retailers may need inventory management tools for seasonal trends, while grocery stores may need systems for managing perishable goods. Ensure the ERP system you choose caters to your industry’s specific needs.
- Budget: ERP systems come in various price ranges, so it’s essential to set a realistic budget. Consider the cost of the software, implementation, training, and ongoing support when making your decision. Remember that investing in a robust system can yield significant long-term benefits.
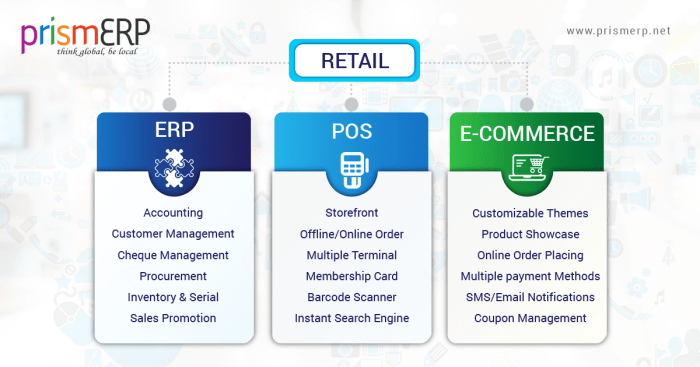
- Integration Capabilities: Your ERP system should seamlessly integrate with your existing systems, such as point-of-sale (POS), e-commerce platforms, and accounting software. Look for systems with strong integration capabilities to avoid data silos and streamline your operations.
Comparing Different ERP Solutions, ERP software for retail businesses with multiple locations
The market offers a wide array of ERP solutions, each with its strengths and weaknesses. To make an informed decision, it’s essential to compare different options based on your specific needs.
- Cloud-Based ERP: Cloud-based ERP solutions are hosted on remote servers, offering accessibility from anywhere with an internet connection. They are typically more affordable and easier to implement than on-premise solutions. However, they may have limited customization options and rely on internet connectivity.
- On-Premise ERP: On-premise ERP systems are installed on your company’s servers, offering greater control over data and customization options. However, they require significant upfront investment and IT expertise for installation and maintenance.
- Industry-Specific ERP: Some ERP solutions are designed specifically for certain retail industries, offering tailored features and functionalities. These systems may provide deeper insights and better cater to industry-specific needs, but they may be less flexible for businesses operating in multiple industries.
Evaluating ERP Software Vendors
Once you have narrowed down your choices, it’s crucial to evaluate the vendors behind the ERP solutions. This includes assessing their reputation, experience, customer support, and implementation process.
- Reputation: Research the vendor’s track record, customer reviews, and industry recognition. Look for vendors with a proven track record of successful implementations and positive customer experiences.
- Experience: Consider the vendor’s experience in the retail industry. Look for vendors who have a deep understanding of your industry’s specific needs and challenges. Their expertise can be invaluable during the implementation process.
- Customer Support: Evaluate the vendor’s customer support offerings, including availability, responsiveness, and knowledge base. Look for vendors who provide comprehensive support, including training and ongoing maintenance.
- Implementation Process: Inquire about the vendor’s implementation process, including timelines, resources required, and communication channels. Choose a vendor with a clear and structured implementation process to ensure a smooth transition.
Implementing and Managing ERP Software
Implementing an ERP system is a significant undertaking for any retail business, especially those with multiple locations. It requires careful planning, execution, and ongoing management to ensure a successful transition and maximize the return on investment.
Implementation Steps
The implementation process typically involves several key steps:
- Project Planning and Scoping: Define project goals, scope, timeline, and resources. Identify key stakeholders and establish clear communication channels.
- Data Migration: Transfer existing data from legacy systems to the new ERP platform. This includes customer data, product information, inventory levels, sales history, and financial records. Ensure data accuracy and completeness to avoid errors and inconsistencies.
- System Configuration: Configure the ERP system to meet the specific needs of the business, including customizing workflows, setting up security roles, and defining reporting parameters.
- User Training: Provide comprehensive training to all users on how to navigate and use the new ERP system effectively. Offer different training formats (e.g., online modules, classroom sessions, hands-on workshops) to cater to various learning styles.
- Testing and Go-Live: Thoroughly test the system to ensure it functions as expected and meets all business requirements. Develop a go-live plan and implement the system in a phased approach to minimize disruptions.
Managing ERP Systems
Effective ERP management is crucial for ensuring long-term success. Here are some best practices:
- Ongoing Maintenance: Regularly update the ERP system with the latest software patches, security updates, and feature enhancements. This helps maintain system stability, performance, and security.
- User Support: Provide prompt and efficient support to users who encounter issues or have questions. Establish a help desk or support portal to streamline communication and resolve problems quickly.
- Data Security: Implement robust security measures to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access, breaches, and cyberattacks. This includes access control, encryption, and regular security audits.
- Performance Monitoring: Monitor system performance regularly to identify bottlenecks, areas for optimization, and potential issues. Use performance dashboards and reports to track key metrics and ensure optimal system efficiency.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly review and assess the ERP system’s effectiveness in meeting business needs. Identify areas for improvement and implement changes to optimize processes, enhance efficiency, and maximize ROI.
Ensuring a Smooth Transition
Several strategies can help ensure a smooth transition to a new ERP system:
- Engage Key Stakeholders: Involve key stakeholders from all departments and locations in the implementation process. This ensures buy-in, addresses concerns, and facilitates communication.
- Phased Rollout: Implement the ERP system in a phased approach, starting with a pilot group or a single location. This allows for testing, feedback, and adjustments before a full rollout.
- Change Management: Communicate clearly about the benefits and changes associated with the new ERP system. Provide ongoing support and training to help users adapt to the new system.
- Data Backup and Recovery: Implement robust data backup and recovery procedures to protect data integrity and ensure business continuity in case of system failures or disruptions.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies

The power of ERP software for retail businesses with multiple locations is best understood through real-world examples. These case studies showcase how businesses have leveraged ERP systems to overcome challenges, boost efficiency, and achieve remarkable results.
Success Stories of ERP Implementation in Retail
- Retail Giant Achieves Streamlined Operations: A major retail chain with over 100 stores implemented an ERP system to centralize its inventory management, streamline purchasing, and improve customer service. The ERP system allowed for real-time inventory visibility across all locations, eliminating stockouts and overstocking. This resulted in a significant reduction in inventory carrying costs and an increase in sales due to better stock availability.
The ERP system also enabled the company to optimize its supply chain, leading to faster delivery times and improved customer satisfaction.
- Small Apparel Retailer Boosts Efficiency: A small apparel retailer with three stores implemented an ERP system to automate its accounting processes, track sales performance, and manage customer data. The ERP system simplified tasks like invoicing, payroll, and inventory management, freeing up the owner’s time to focus on other aspects of the business. The system also provided valuable insights into sales trends, allowing the owner to make data-driven decisions about inventory purchasing and marketing campaigns.
This resulted in a significant increase in sales and improved profitability.
- Restaurant Chain Improves Customer Experience: A restaurant chain with multiple locations implemented an ERP system to manage reservations, track customer orders, and analyze customer feedback. The system enabled the chain to personalize the dining experience for its customers, offering tailored recommendations and special offers based on their preferences. It also helped to improve communication between the kitchen and the front of house, reducing wait times and ensuring a smoother dining experience.
This resulted in increased customer satisfaction and repeat business.
Challenges and Solutions in ERP Implementation
- Data Migration and Integration: Migrating data from legacy systems to the new ERP platform can be a complex and time-consuming process. Many businesses face challenges in ensuring data accuracy and consistency during the migration. To overcome this, it is essential to have a well-defined data migration plan, including data cleansing, validation, and testing. Working with an experienced ERP implementation partner can also help to streamline the process and minimize risks.
- User Adoption and Training: Successful ERP implementation requires user buy-in and effective training. Many businesses struggle to get employees to adopt the new system and utilize its full potential. To address this, it is crucial to provide comprehensive training programs that are tailored to the specific needs of different user groups. It is also important to involve employees in the implementation process, soliciting their feedback and addressing their concerns.
- Customization and Integration: ERP systems are often complex and require customization to meet the specific needs of a retail business. Integrating the ERP system with existing systems, such as point-of-sale (POS) systems, can also pose challenges. To overcome these challenges, businesses should choose an ERP system that offers flexible customization options and a robust integration platform. Working with an experienced implementation partner can also help to ensure a smooth integration process.
In the competitive retail landscape, ERP software emerges as a powerful tool for multi-location businesses seeking to thrive. By harnessing the capabilities of a robust ERP system, retailers can gain a competitive edge, optimize their operations, and deliver exceptional customer experiences. With its ability to unify operations, provide real-time insights, and enhance decision-making, ERP software paves the way for sustainable growth and success in the dynamic retail world.
FAQs: ERP Software For Retail Businesses With Multiple Locations
What are the main benefits of using ERP software for multi-location retail businesses?
The main benefits include improved inventory management, real-time data visibility, enhanced customer service, streamlined operations, reduced costs, and increased profitability.
How much does ERP software cost for retail businesses?
The cost of ERP software varies depending on the size of your business, the features you need, and the vendor you choose. It’s essential to research different options and compare pricing models to find the best fit for your budget.
What are some popular ERP software solutions for retail businesses?
Some popular ERP software solutions for retail businesses include SAP, Oracle, Microsoft Dynamics, NetSuite, and Acumatica. Each solution has its own strengths and weaknesses, so it’s important to research and compare them based on your specific needs.
How long does it take to implement an ERP system?
The implementation time for an ERP system can vary depending on the complexity of your business, the chosen software, and the resources available. It’s generally recommended to allocate sufficient time for data migration, training, and system configuration.